Clinical features
- Demographics
- Africa: associated with EBV; common in children
- South China: most common cancer in adults; rare in children
- US: rare in adults and children
- Associated with HBV infection and repeated exposure
- Presentation as a lymph node metastasis is frequent
- Other sites of metastasis: bone, bone marrow, liver and lungs
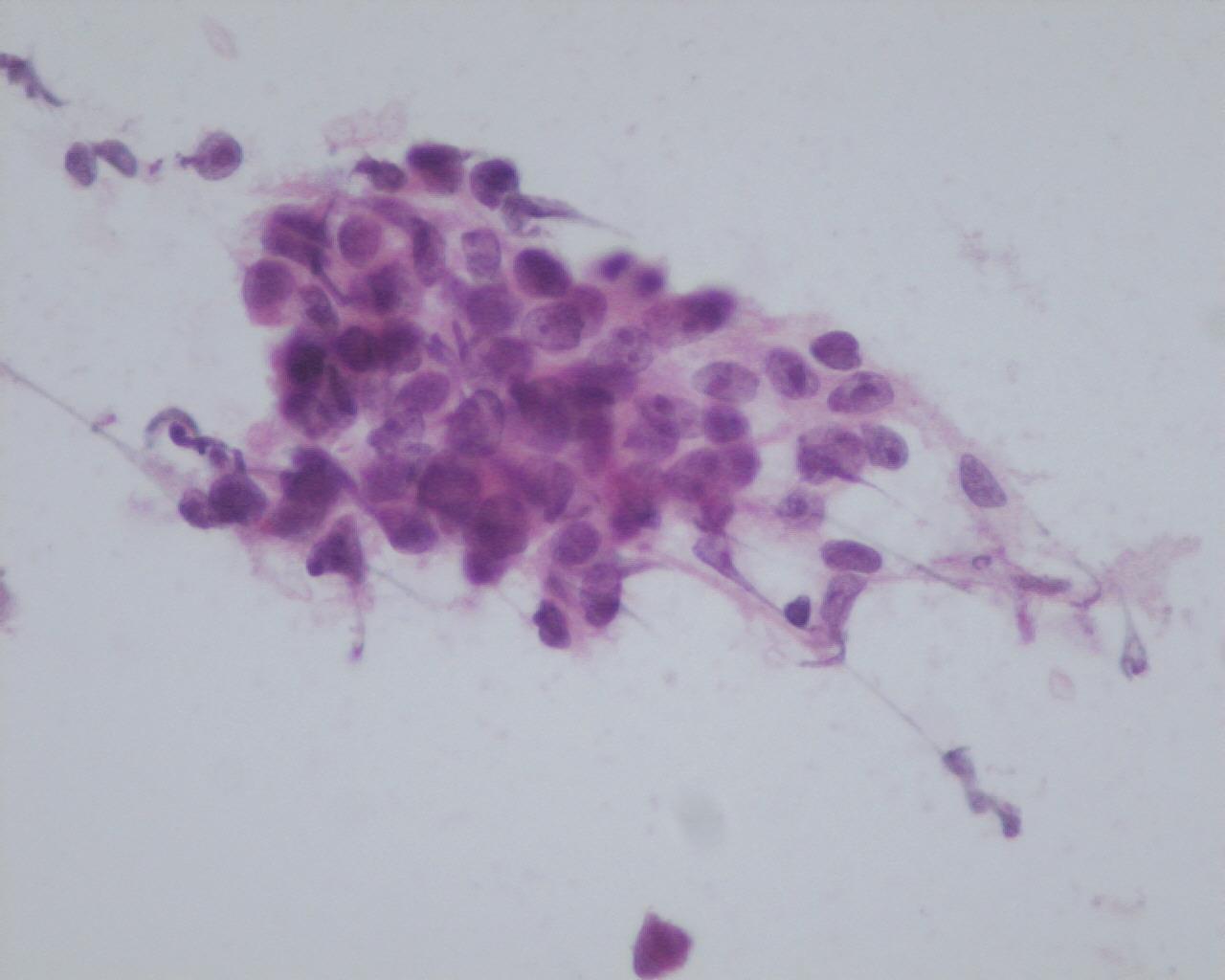
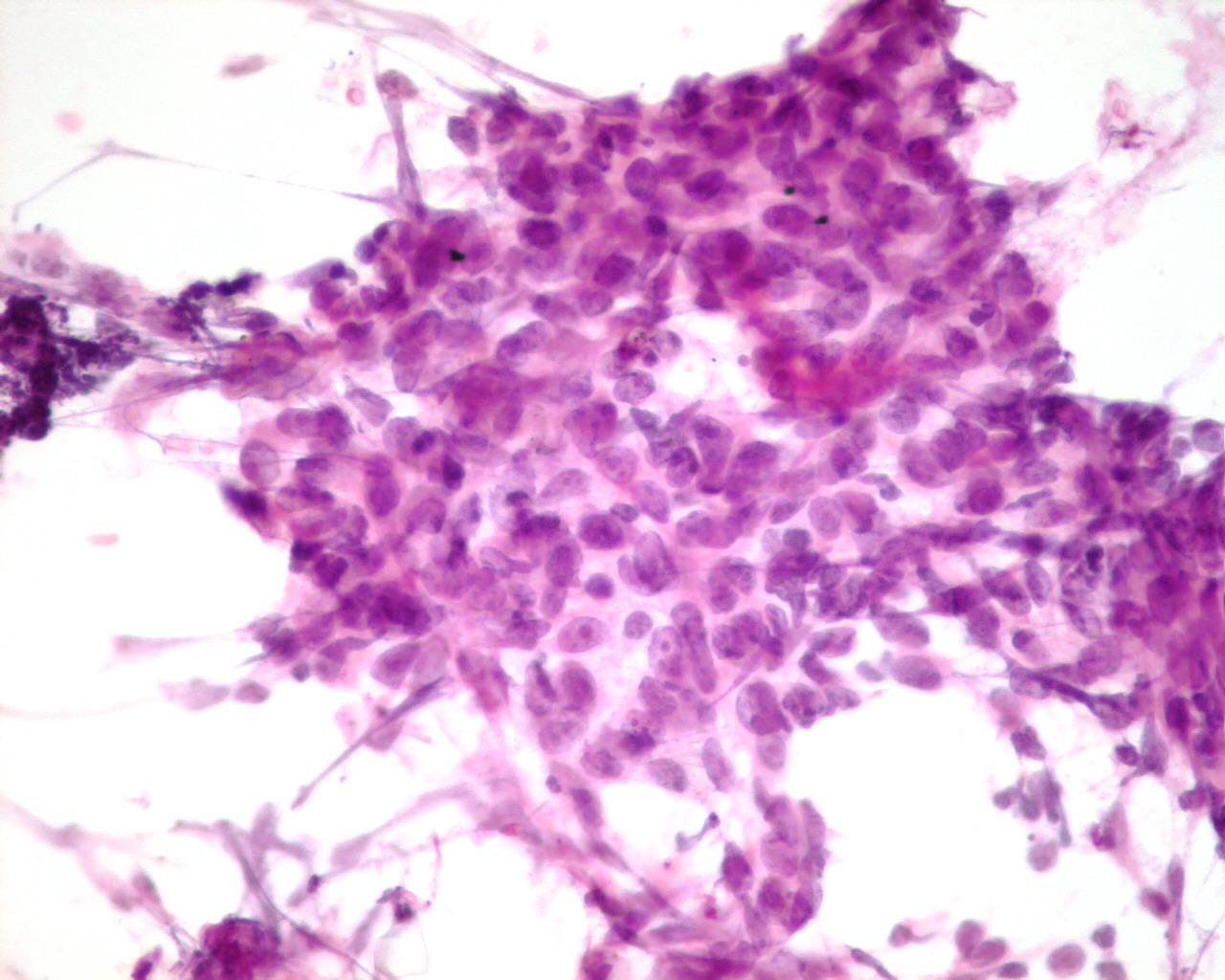
Fig 104a – Nasopharyngeal carcinoma – Sheets of undifferentiated epithelial cells, with high nuclear/cytoplasmic ratio, vesicular nuclei and prominent nucleoli (H&E)
- Sheets and clusters of undifferentiated epithelial cells
- Vesicular nuclei and prominent nucleoli
- Sparse eosinophilic cytoplasm
- Inflammatory cells: lymphocytes (often T lymphocytes) and plasma cells
Immunocytochemistry
- Keratins: positive
- EMA: positive
- EBV: positive
- EBER: positive
- CD23: positive in some cases
- CD30: positive (in rare cases)
- CEA: variable
- S-100 protein: variable
Genetic studies
- Over expression of p53
Differential diagnosis
- Large cell lymphoma
- EMA: useless for the differential diagnosis with large cell lymphoma
- CD30: useless for the differential diagnosis with large cell lymphoma
- Hodgkin’s disease
- Sternberg-Reed cells
- CD15: positive
Main points
- Treatment: radiation therapy
- Good prognostic factors: younger age, lower stage, metastases limited to the upper neck and no involvement of central nerve system