Clinical features
- Rare tumour accounting for 0.17% to 2% of all nonendocrine tumours of the pancreas
- Adolescents girls and young women
- Benign tumour
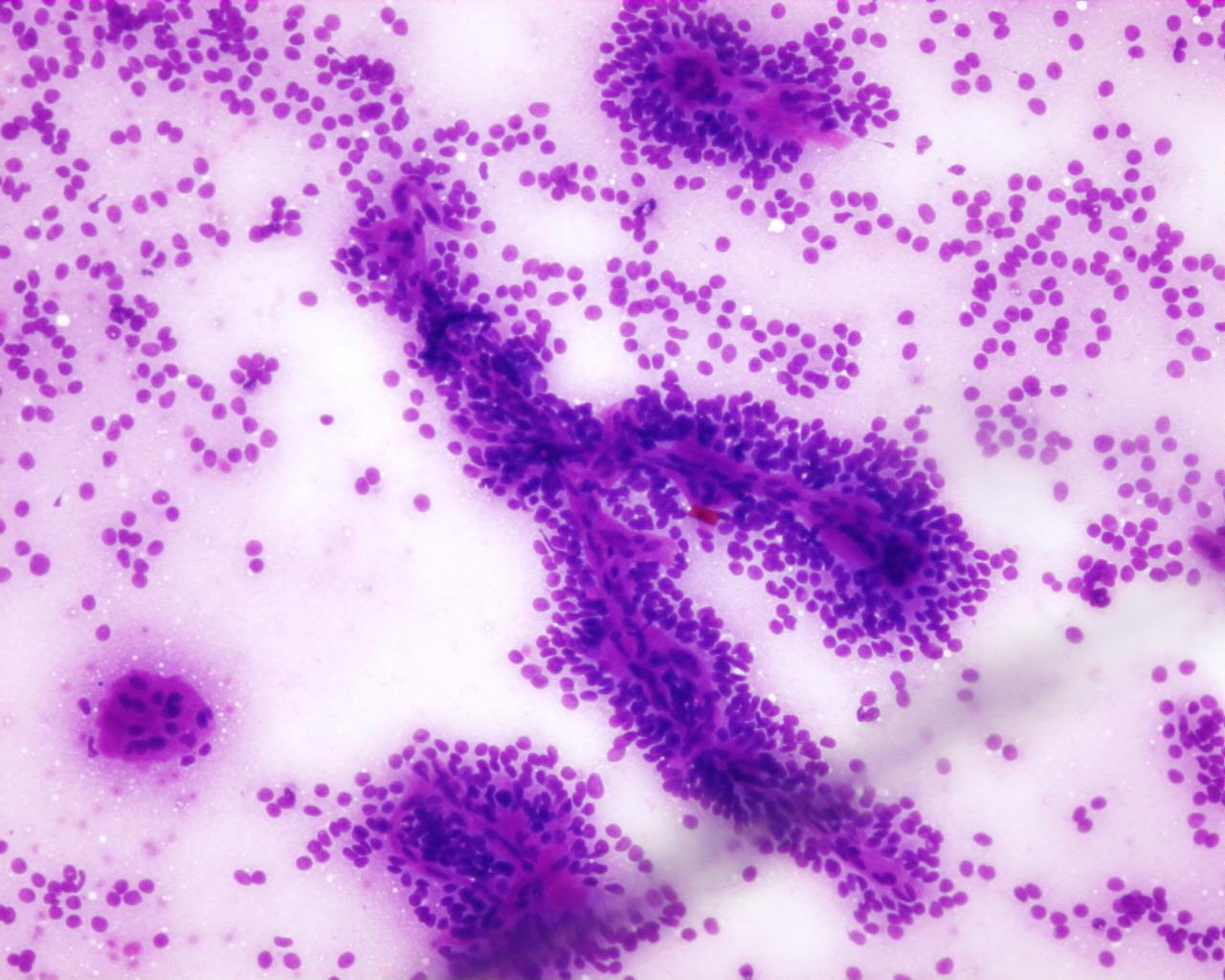
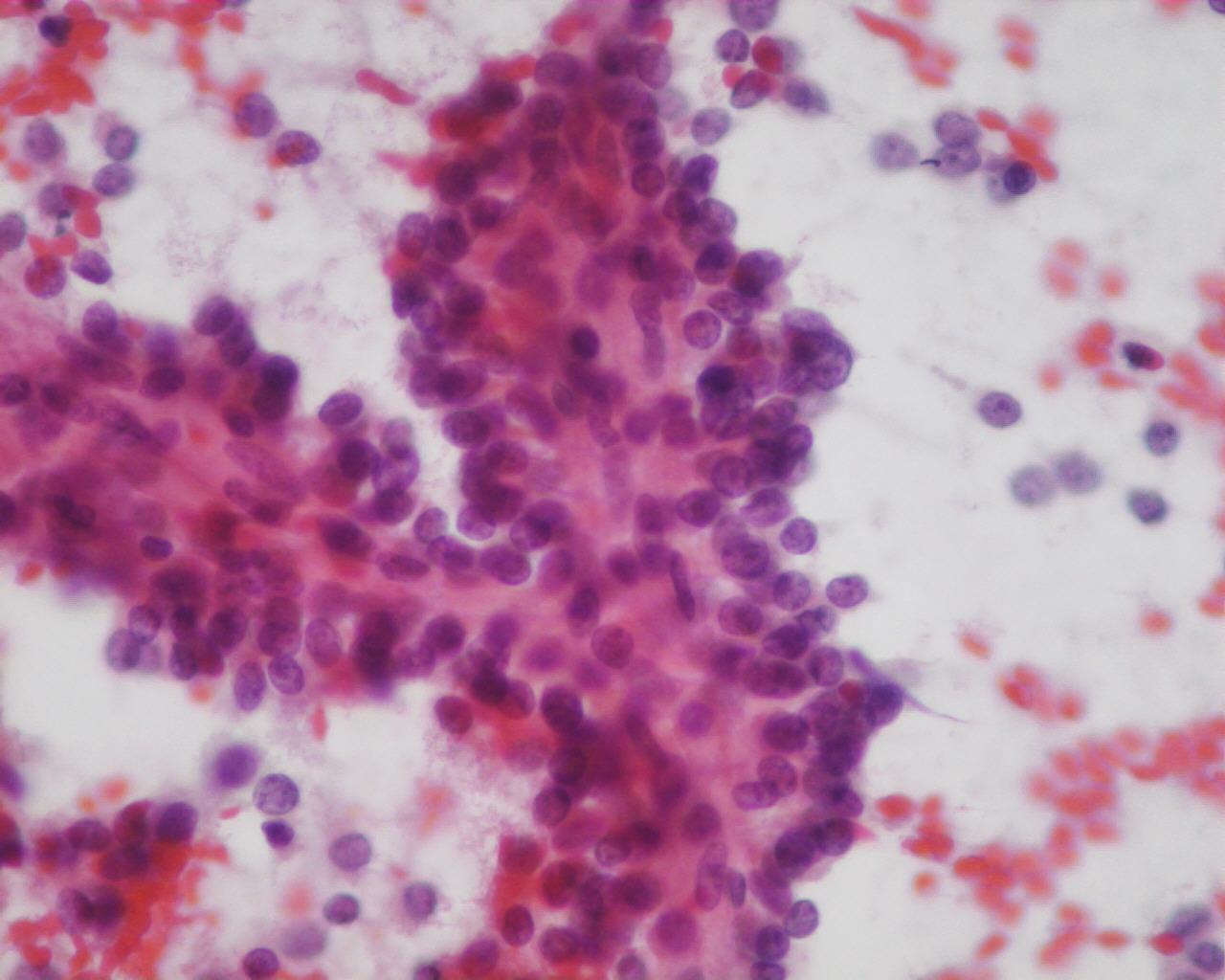
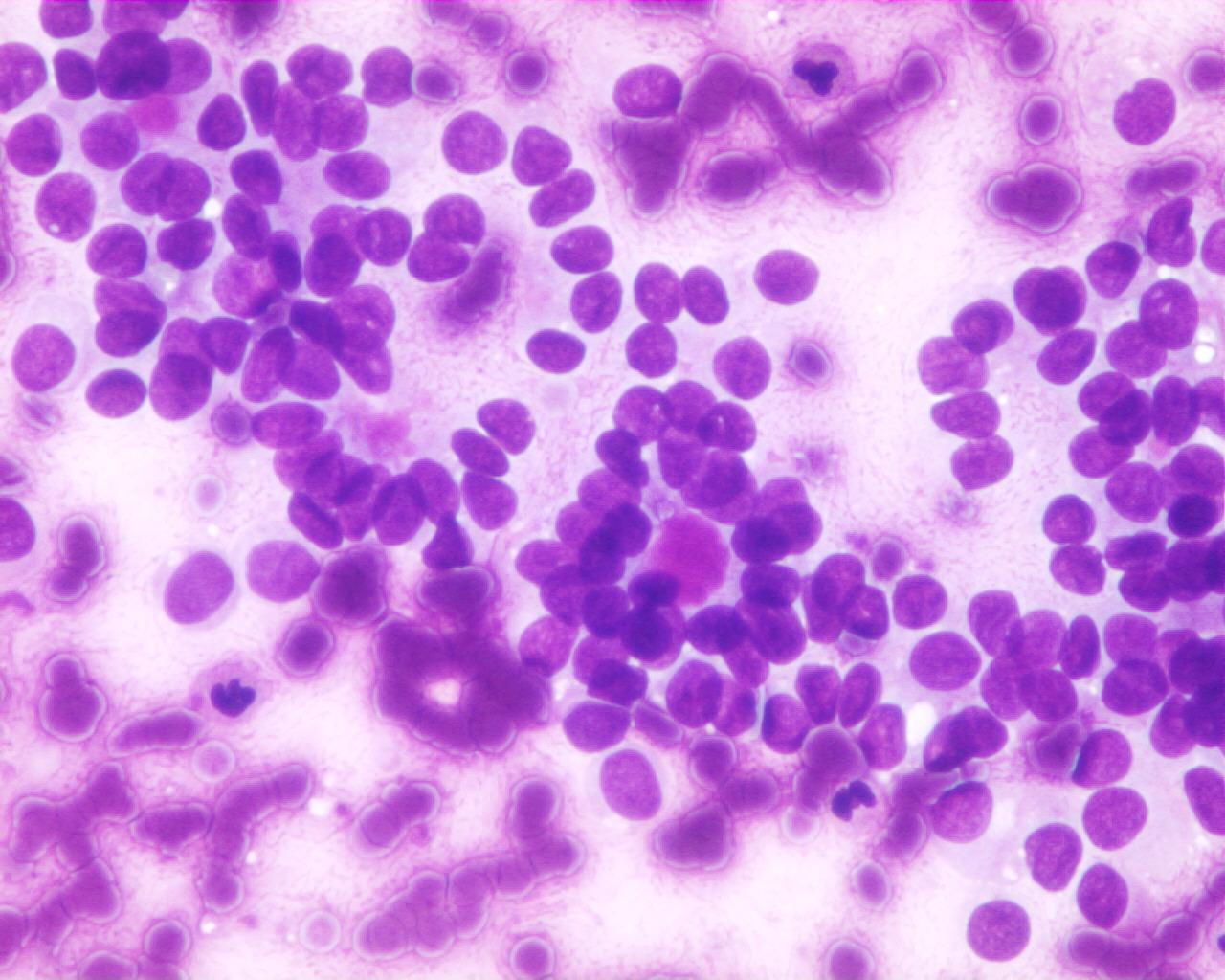
Fig 83- Solid –pseudopapillary neoplasm -– Delicate papillary groups (Giemsa)
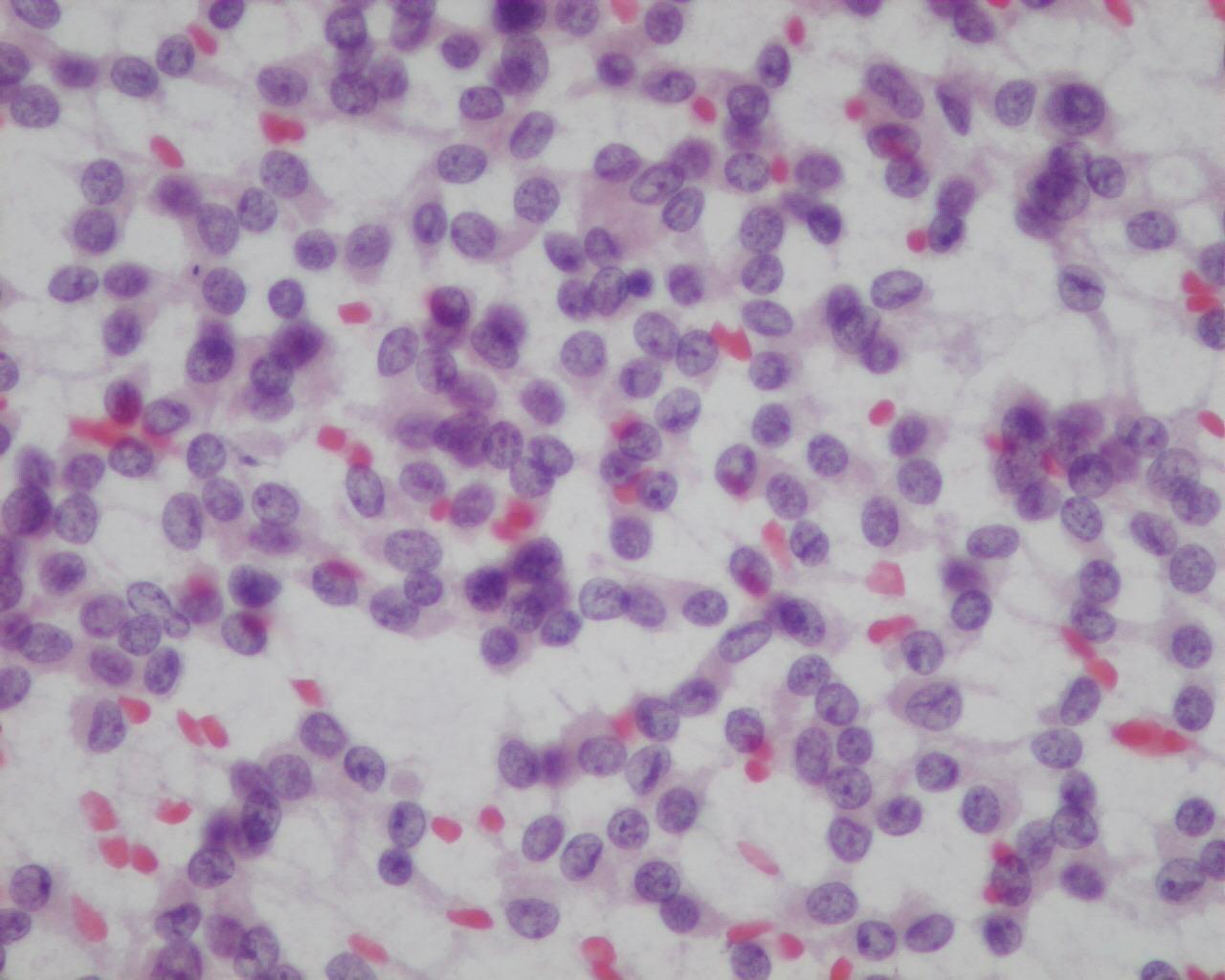
- Branching delicate papillary structures covered by monomorphic tumour cells
- Individual scattered cells
- Nuclei with fine chromatin and small nucleoli
- Nuclear grooves
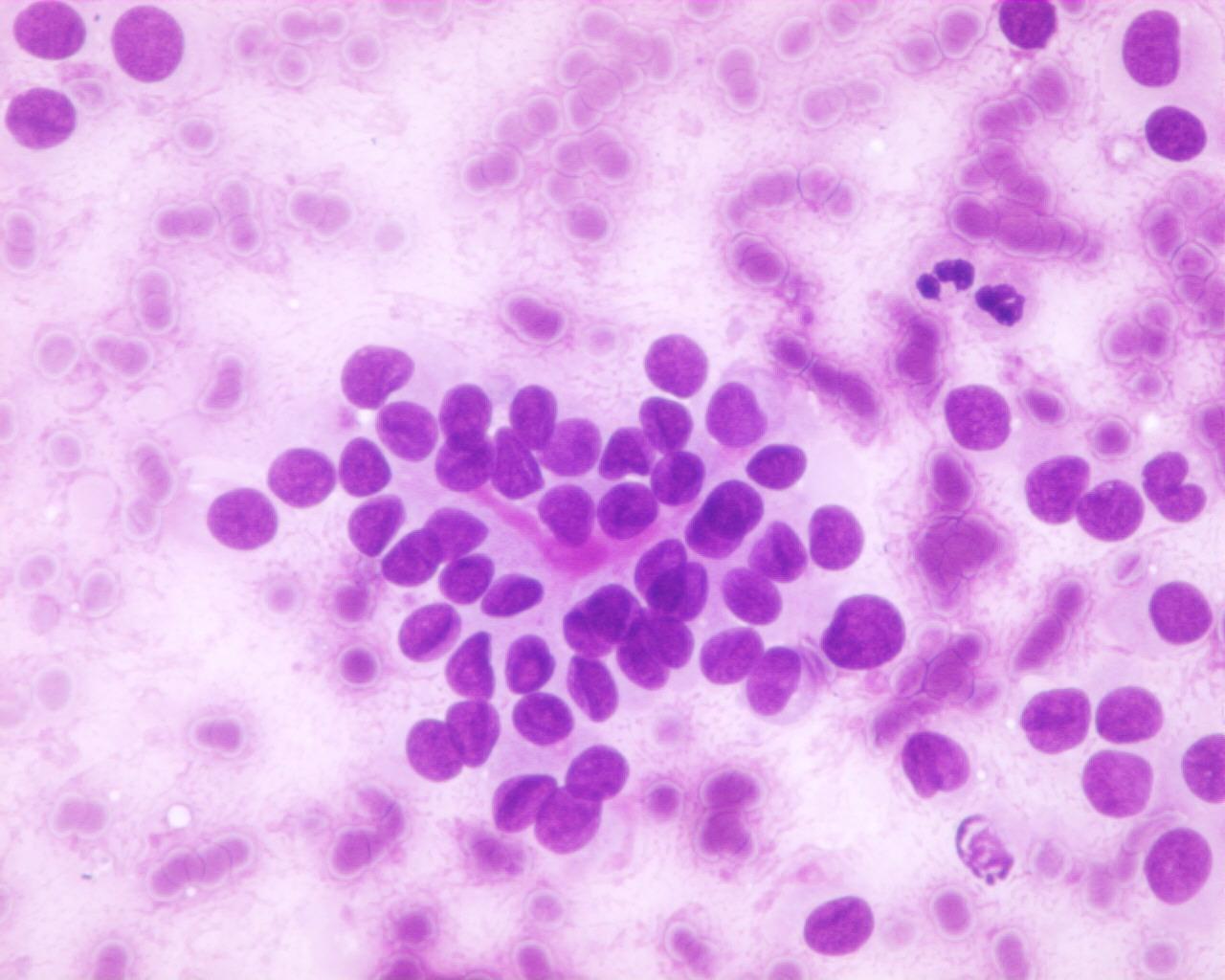
- Foamy histiocytes
- Multinucleated giant cells
- Diastase-resistant PAS-positive hyaline globules
Immunocytochemistry
- Vimentin: Positive
- NSE: Positive
- Synaptophysin: Positive
- Alpha1-antitrypsin :Positive intracytoplasmic globules
- Alpha1-antichymotrypsin:Positive intracytoplasmic globules
- CD56- Positive-Intense and diffuse
- CD10: Positive
- Chromogranin: negative
- CEA: Negative
Genetic Studies
- Most tumours are diploid
Differential Diagnosis
- Mucinous cystic neoplasms /microcystic adenomas
- Presence of mucoid material in the background
- Acinar cell carcinoma
- Older patients
- No female predominance
- Cytological atypia
Main points
- 95% cure after resection
- All the attempts to predict an aggressive behaviour have been unsuccessful
- In 10% of the cases it can metastasize to the liver and peritoneum, generally associated to venous invasion and high grade