Clinical features
- Malignant mesenchymal neoplasm
- Rare renal tumour (3-5% of all paediatric kidney tumours)
- It occurs almost exclusively between the ages of 6 months and two years
- Male predominance
- Not associated with malformations or syndromes
- Propensity for bone (skull) and visceral metastasis
- Single-centre tumour
- High-risk tumour (SIOP-2001 revised working classification of renal tumours of childhood)
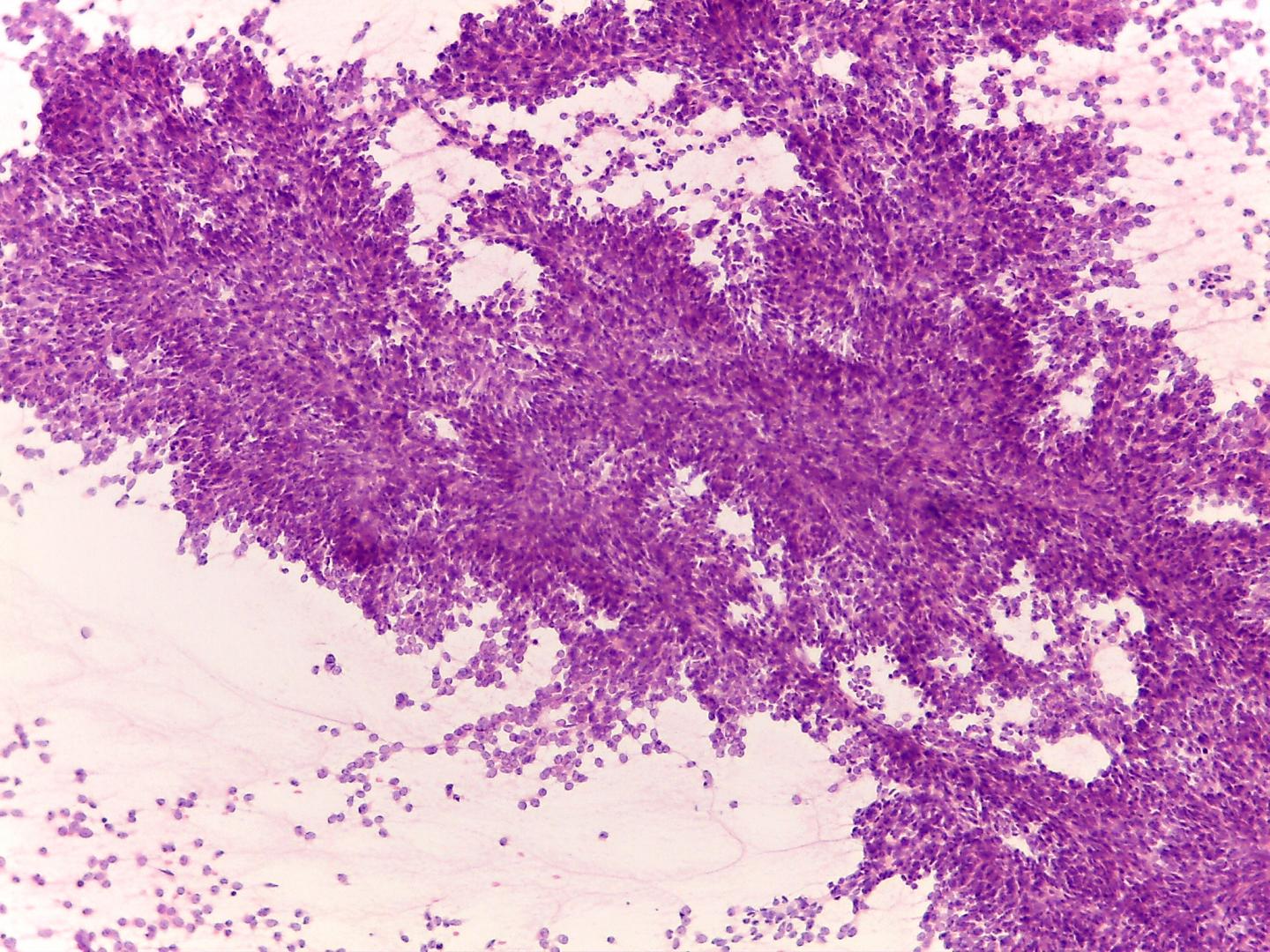
Fig 9a – Clear cell sarcoma of the kidney- Cords of polygonal cells. Remark the chicken wire vasculature (H&E)
- Variable cellularity
- Background with metachromatic mucoid-like material rich in glycoproteins, seen in Giemsa-stained slides
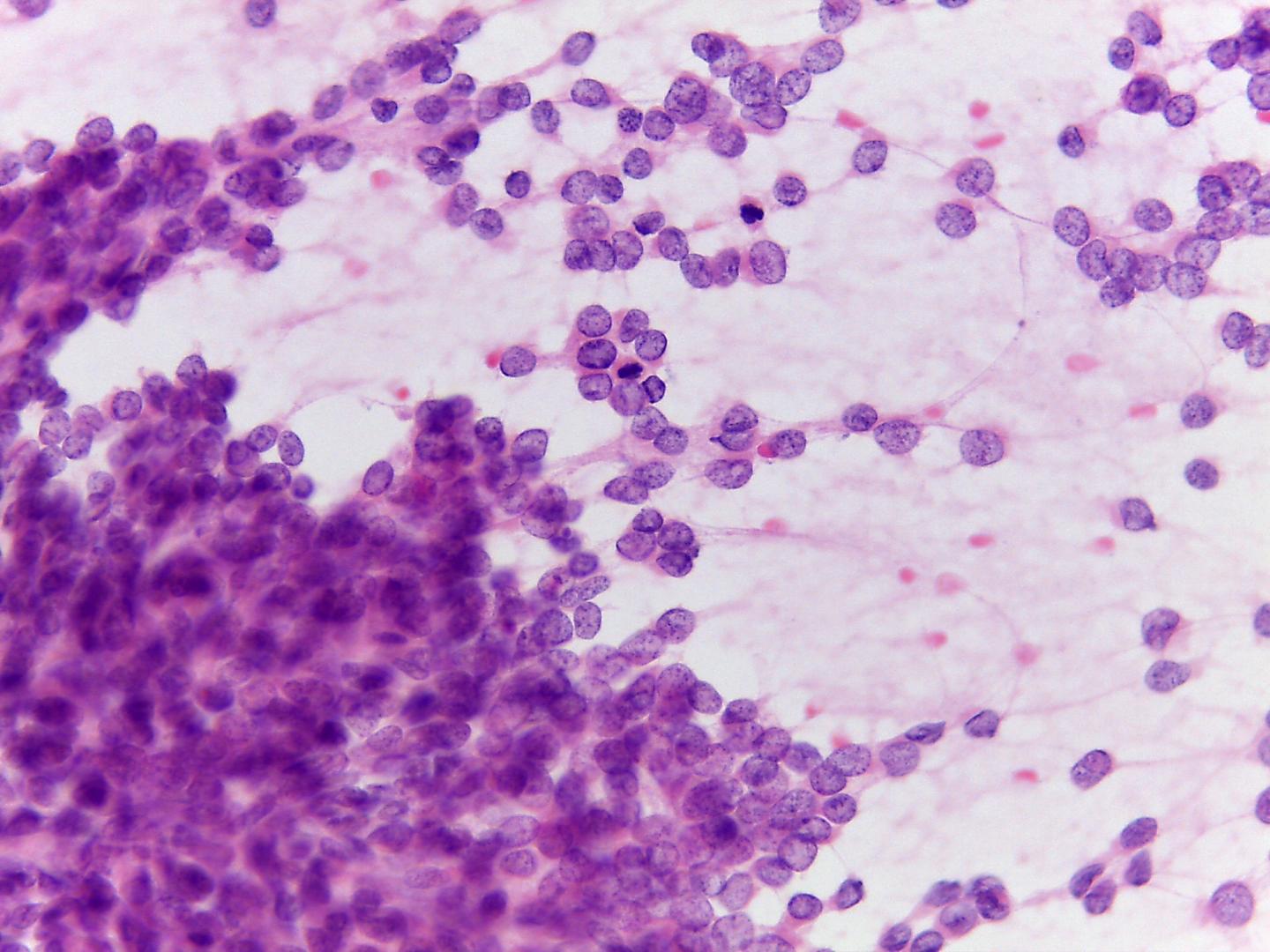
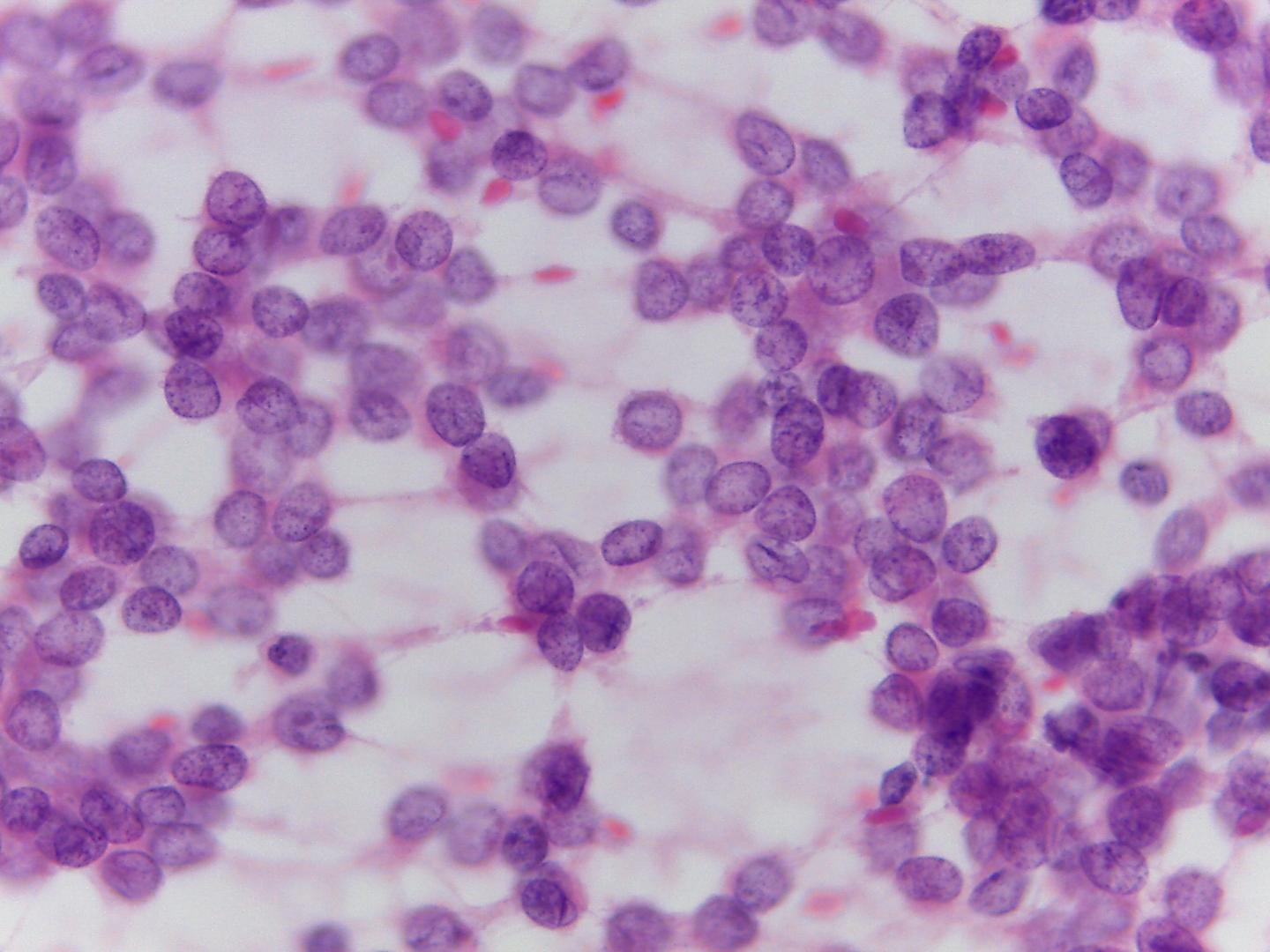
- Large cells that are dispersed or in perivascular pattern
- Round, oval or short spindle bland nuclei with vesicular chromatin
- Nuclear grooves sometimes present
- Inconspicuous nucleoli
- Fragile and pale cytoplasm
- Myxoid stroma may be present
- Necrosis
- The presence of confounding renal tubules entrapped by the tumour that can appear in the smears, can lead to erroneous diagnosis of Wilms´ tumour (these tubules are CD56(NCAM) negative and EMA positive
Immunocytochemistry
- Vimentin: positive, but moderate not strong- “ ….a strong positive Vimentin points away CCSK”
- CD56 (NCAM)-positive (diffuse)
- CD99: negative
- CD117 :positive
- Bcl2: positive
- EMA: negative
- Desmin: negative
- CD10:negative (rare cases reported as positive)
- CD15:negative
- WT1: negative
Differential diagnosis
- Nephroblastoma (blastemal type)
- Regular nuclei with fine chromatin
- Cytoplasm is very scarce (cells in CCS bare more cytoplasm)
- Sometimes epithelial markers can show poorly differentiated or isolated cells with epithelial differentiation
- WT1: Positive
- Mesoblastic nephroma
- Generally diagnosed within the first six months of life
- Bland, small spindle cells
- CD56 (NCAM): negative
- WT1: positive (cytoplasm)
- Neuroblastoma
- Nuclei with salt-and-pepper chromatin
- Neuroblasts at different stages of maturation
- Fibrillary matrix
- Vimentin: usually negative
- Synaptophysin: positive
- NSE: positive
- PNET
- Most common in young adults
- Nuclei with coarse chromatin
- CD99: positive
- t (11:22) (q24; q12)
- Rhabdoid tumour
- Cells with a rhabdoid-like pattern:
- Prominent eosinophilic nucleoli
- Eosinophilic para nuclear cytoplasmic inclusions
- Cytokeratin’s: positive
- CD56(NCAM): negative
- INI 1: negative
- Cells with a rhabdoid-like pattern:
Main points
- Undifferentiated sarcoma, nearly exclusively in the kidneys
- No familial specific malformations, syndromes or genetic abnormalities associated
- Poor prognostic changes: necrosis
- Even low-stage tumours have poor prognosis
- Also known as bone-metastasizing renal cell tumour
- Metastasis can occur 3 to 10 years after diagnosis
- Recurring genetic defects have been reported: t(10;17), del(14)(q24.1q31.1)