Clinical features
- In the lung it is the most common isolated primary lesion in patients under 16 years of age
- 56% of the benign lung tumours in children
- Previous history of pulmonary disease
- Usually asymptomatic
- Mainly located in the apical segments of the lower lobes
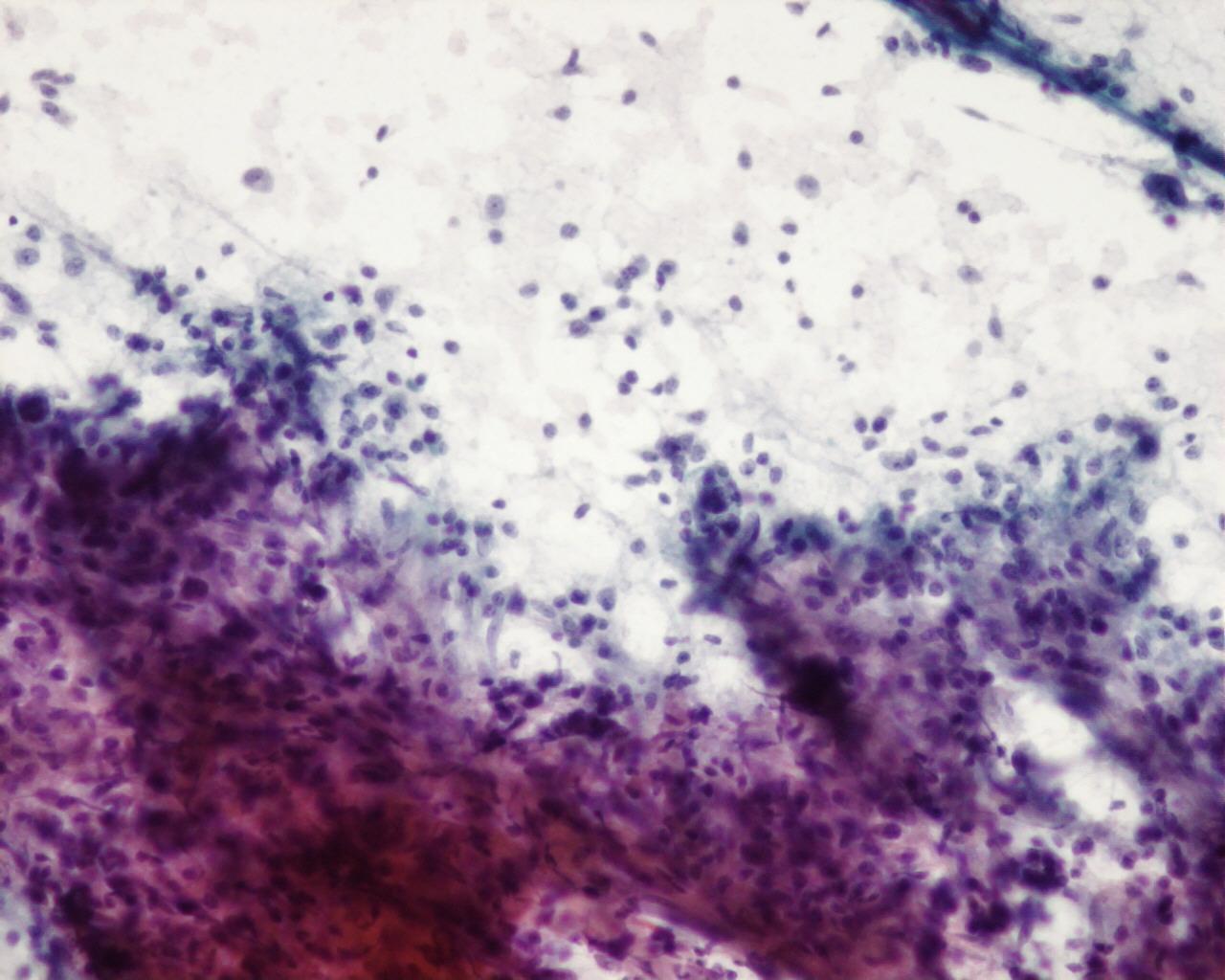
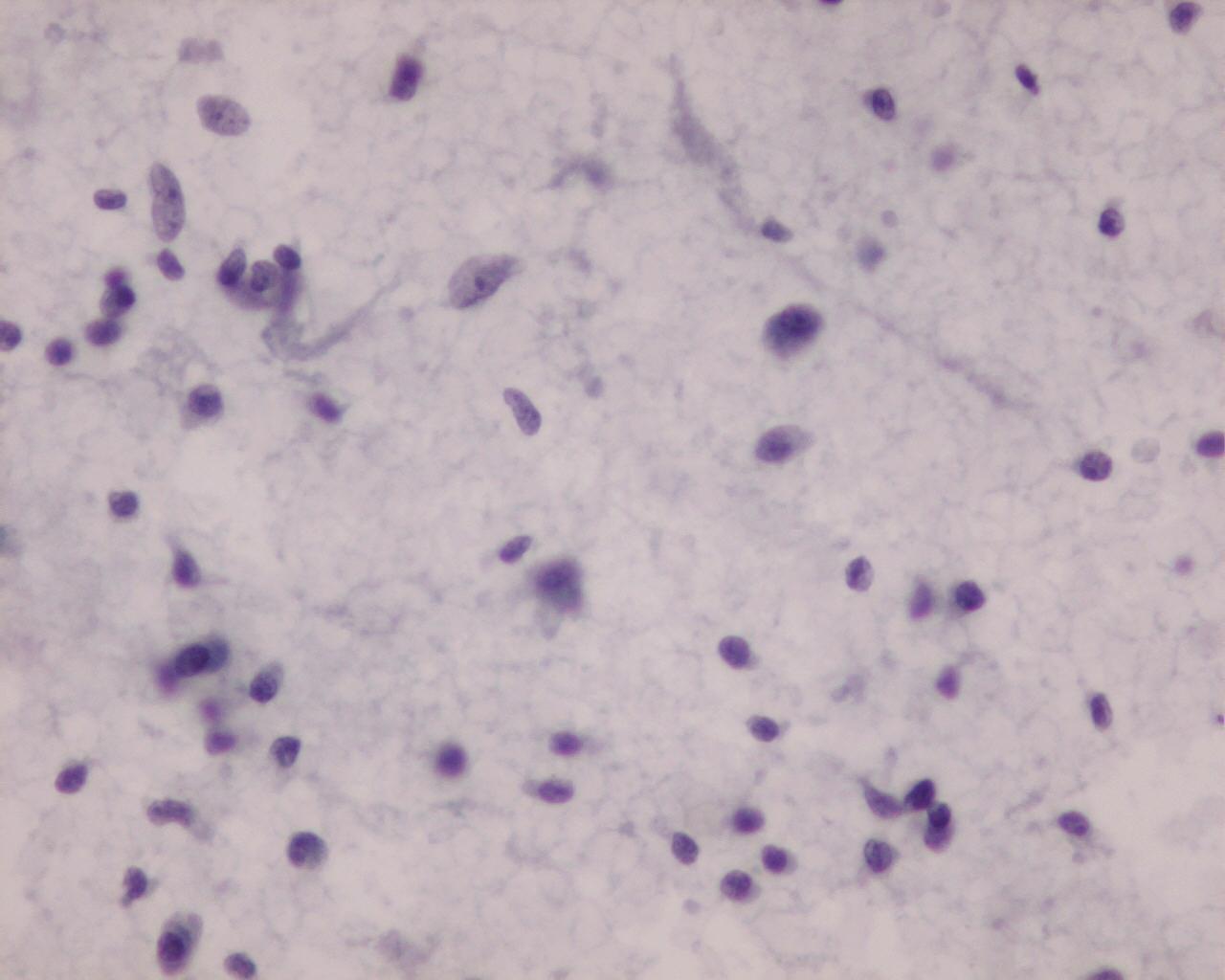
Fig 91 – Inflammatory pseudotumor – Smear from a transthoracic guided fine needle aspiration – Poorly cohesive polymorphic population (fibroblasts, Histiocytes, lymphocytes and plasma cells) (H&E)
- Polymorphic cellular population of:
- Histiocytes
- Fibroblasts
- Lymphocytes
- Plasma cells
Immunocytochemistry
- Confirmation of the myofibroblastic origin of spindle cells:
- Vimentin : Positive
- Desmin: Positive
- Muscle-specific actin: Positive
Modern Techniques of Diagnosis
Non contributory
Differential Diagnosis
- Inflammatory lesions
- Carcinoid (spindle cell pattern)
- Monotonous population of neoplastic cells
- Neuroendocrine “salt and pepper” chromatin
- Absence of inflammatory cells
Main points
- Excision is curative when complete. If not, progression to infiltration of local tissues can be a problem