Clinical features
- Children and young adults
- Serum elevation of alpha-fetoprotein
- Frequently develops from a teratoma
- More common in the ovary than in the testis
- Rare locations: retroperitoneum and mediastinum
- No association with endocrine symptoms
- Malignant-5-year survival-66.6%
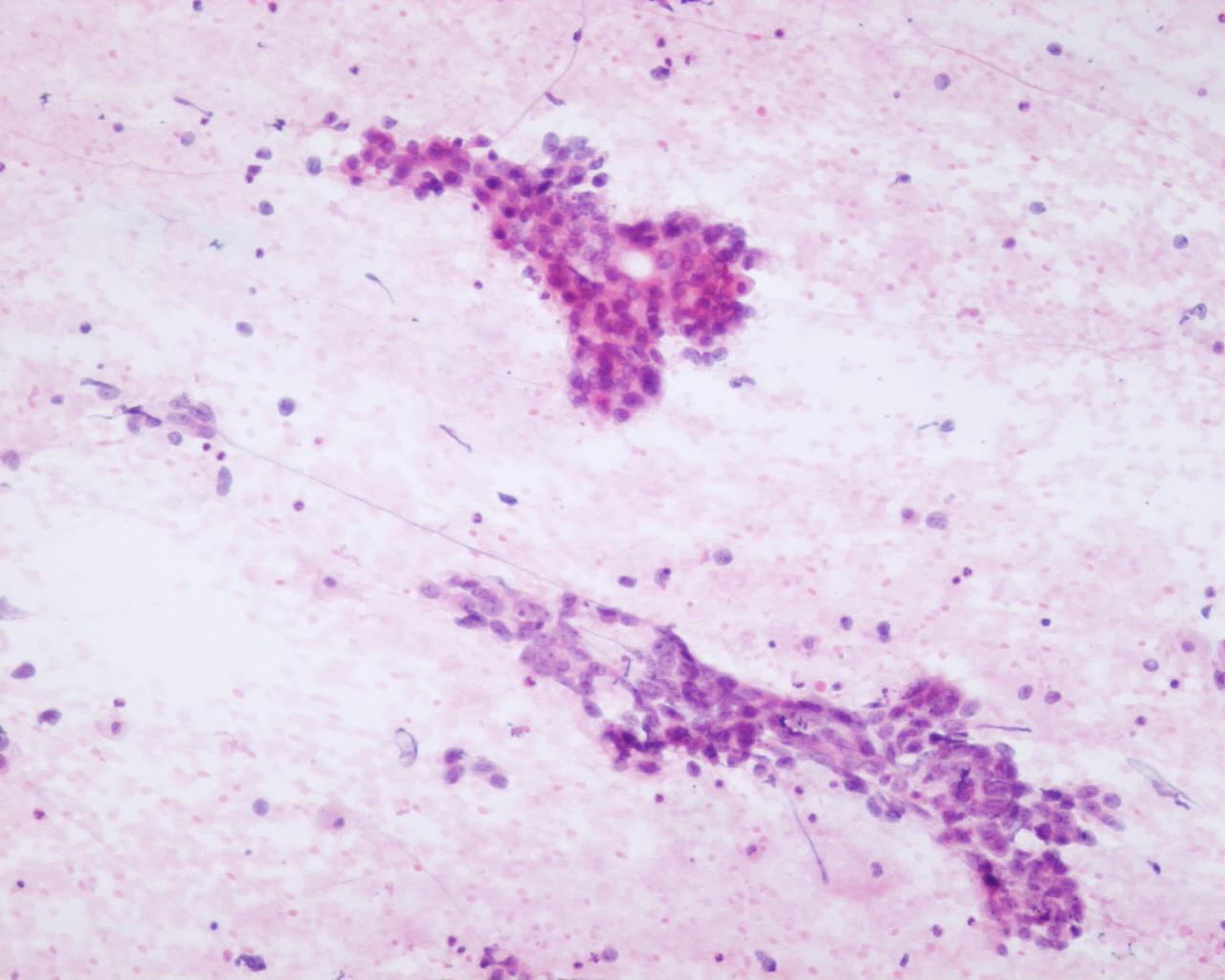
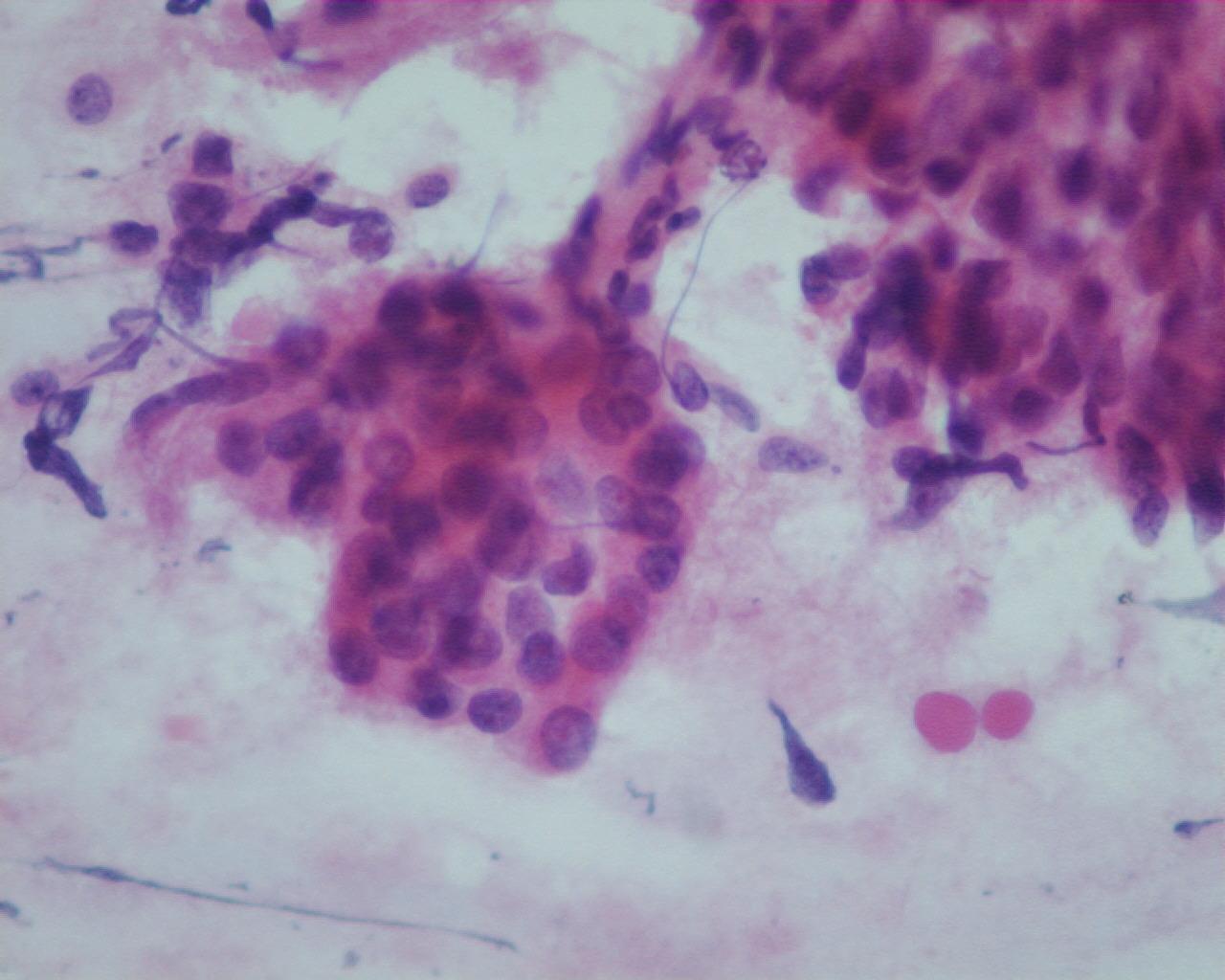
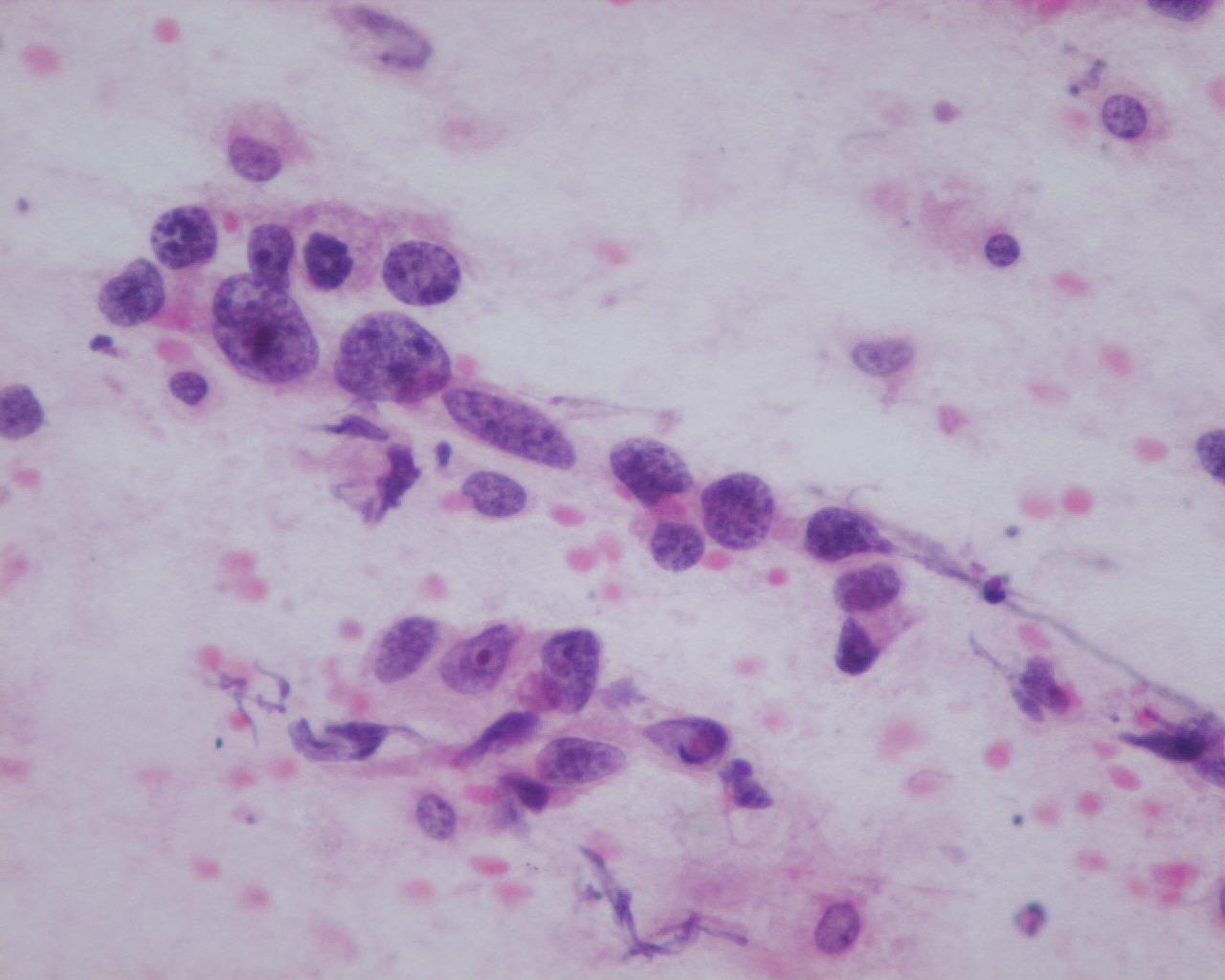
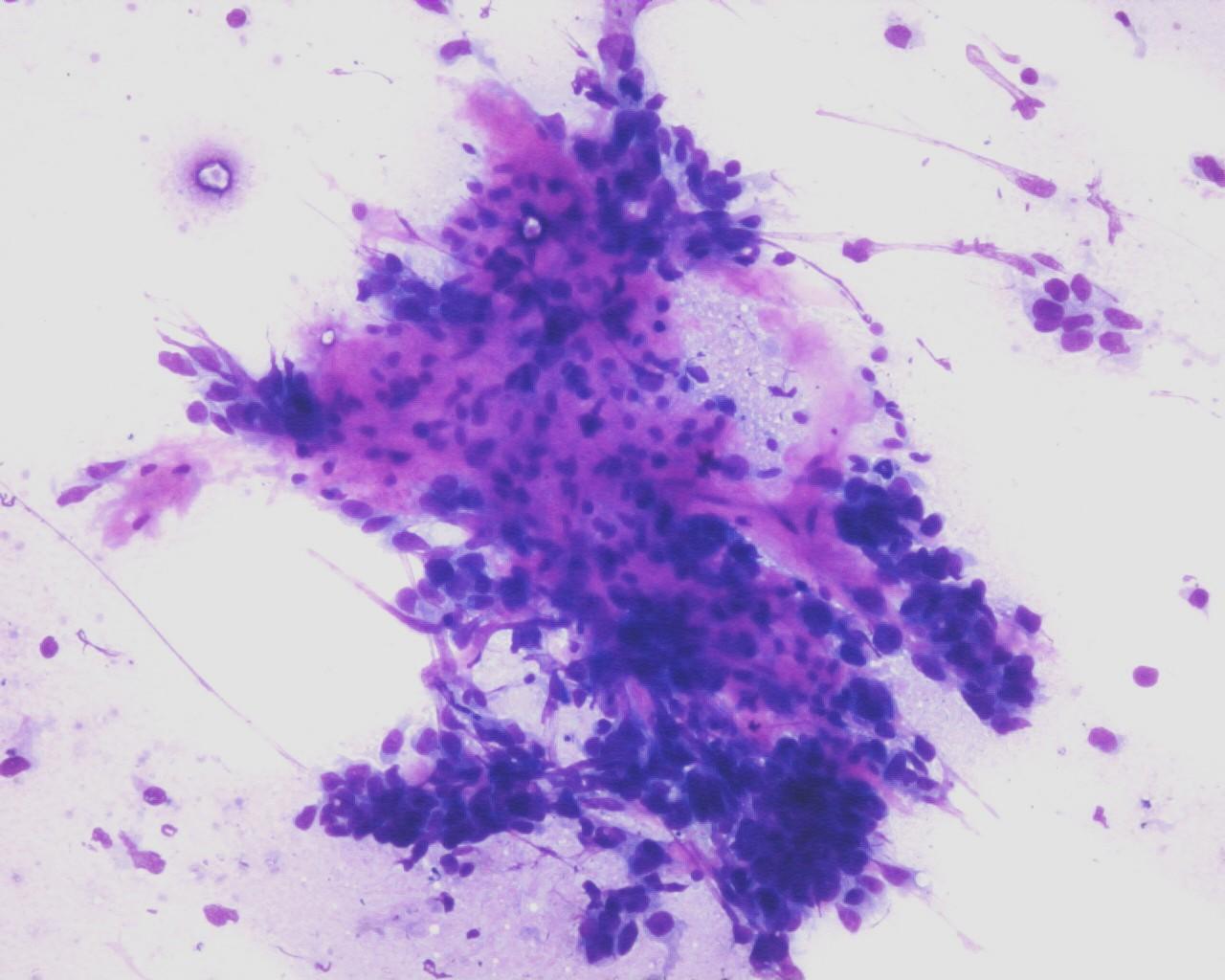
Fig 69- Yolk sac tumor – Papillary aggregates of pleomorphic tumor cells (H&E)
- (Macroscopically aspirates can carry translucent and viscous material
- Moderate to high cellularity
- Cells embedded within the matrix
- Single cells or in spherical or papillary aggregates
- Large polygonal cells
- Hyperchromatic nuclei
- Frequent nucleoli
- Pale cytoplasm with vacuoles of glycogen
- Mucoid background
- Dense basement membrane-like matrix
- Eosinophilic hyaline globules in intra or extracellular location
- Necrosis
Immunocytochemistry (see Table 1)
- Alpha-fetoprotein: positive
- Alpha-1-antitrypsin: positive (focal)
- CEA: positive
- Cytokeratin: positive
- PLAP: positive
- Human chorionic gonadotropin: negative
- Vimentin: negative
- CD30: negative
Histochemical stains
- Eosinophilic hyaline globules (PAS-diastase positive)
Differential diagnosis
- Embryonal carcinoma
- Rare presence of hyaline globules
- Absence of dense basement membrane-like matrix
- Alpha-fetoprotein: generally negative
- PLAP: positive
- CD30: positive