Clinical features
- Rare, aggressive malignant tumour
- Children under 6 years of age
- Family history of similar-appearing intrathoracic tumours, or malformations in 30% of the cases (e.g. cystic nephroma, lung cysts)
- Clinical presentation-respiratory distress
- X-ray- cystic or solid/cystic mass in the lung, pleura or mediastinum
- Association to cystic nephroma of the kidney
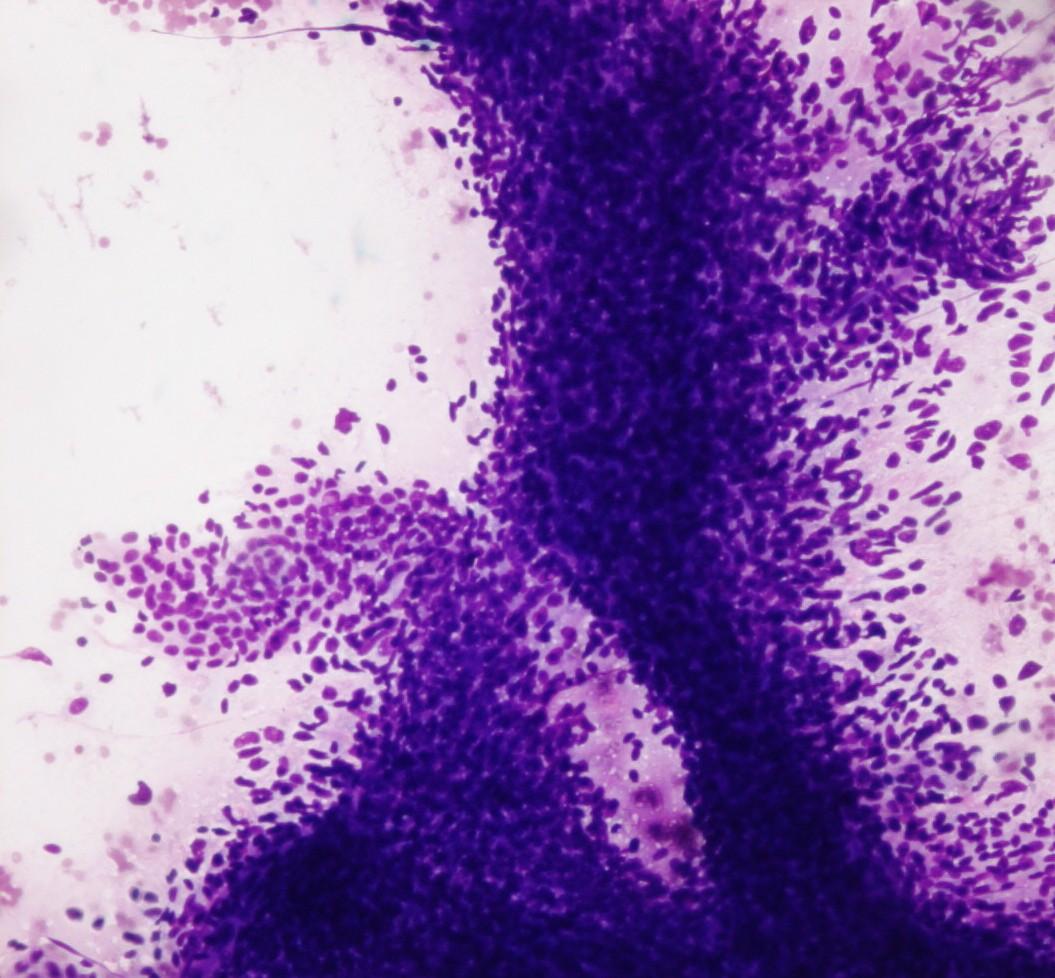
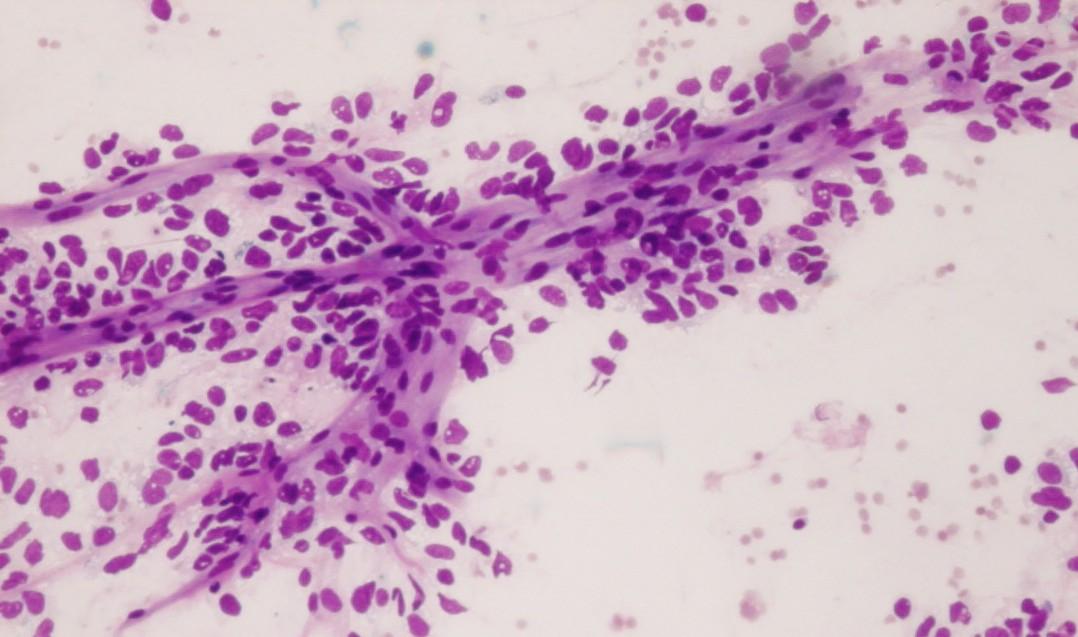
Fig 95 – Pulmonary Blastoma of Childhood – Smear from a transthoracic guided fine needle aspiration composed of a big three-dimensional cellular group of blastematous cells (Giemsa)
- Blastematous cells
- Single or cohesive aggregates
- Small round blue cells
- Small elliptical nuclei
- Fine chromatin
- Inconspicuous nucleoli
- Scant cytoplasm
- Myxoid mesenchymatous stroma
- Uncommitted
- Differentiation: rhabdomyosarcomatous, chondrosarcomatous
- Pleomorphic multinucleated cells have been reported
- Necrosis
- Mitosis
- Hyaline globules (PAS positive, diastase resistant)
Immunocytochemistry
- Cytokeratin: negative
- CD99: Negative
Genetic Studies
- Trisomy 8
Differential Diagnosis
- Cystic adenomatoid malformation/ other benign lung cystic conditions
- Absence of blastema
- PNET
- Most common in older children
- Rosettes
- Absence of mesenchymal differentiation
- CD99: Positive (membranous pattern)
- t(11;22)(q24;q12) – (90% of the cases)
- Metastatic neuroblastoma
- Background of eosinophilic (HE) fibrillary material
- Neuroblasts in varying degrees of maturation
- Rare situation
- Lymphoblastic lymphoma
- Lymphoglandular bodies
- Nuclei with irregular membrane, fine powdery chromatin and inconspicuous nucleoli
- Rhabdomyosarcoma
- When this is the only component present, differential diagnosis is impossible
- Metastatic mesenchymal chondrosarcoma
- It may be indistinguishable
- Desmoplastic small cell tumour
- Coexpression of desmin(dot), cytokeratin (dot), Vimentin and NSE
- EMA : Positive
Main points
- Unknown histogenesis-probably derived from primitive mesenchymal cells in the lung or pleura
- Survival at 5 years- 45%
- Frequent pleural involvement at presentation
- Type I-better prognosis than type II or III
- Progression from type I to type II or III is described