Clinical features
- Rare (less than 5% of paediatric renal tumours)
- Paediatric associated subtypes:
- Renal medullar carcinoma
- Xp11.2 associated RCC represent 20% of renal cell carcinomas at paediatric and adolescent ages
- Special type of renal cell carcinoma
- More frequent in children
- Associated with different translocations involving chromosome Xp11.2.
- t(6;11) translocation RCC
- In tuberous sclerosis setting (TSC)
- Kidney manifestations of TSC: angiomyolipomas, polycystic kidney disease, oncocytomas, RCC
- RCC in TSC: clear cell type; papillary; chromophobe
- Few cases reported
- Neoplastic cells with granular eosinophilic abundant cytoplasm
- Differential diagnosis between RCC NOS, oncocytoma and chromophobe RCC can be a challenge
- HMB45:negative
- AE1/AE3: positive
- Neuroblastoma associated RCC
- Very unusual-2.5% of renal cell carcinomas in young patients
- Described in survivors of childhood neuroblastoma
- High-risk tumour (SIOP-2001 revised working classification of renal tumours of childhood)
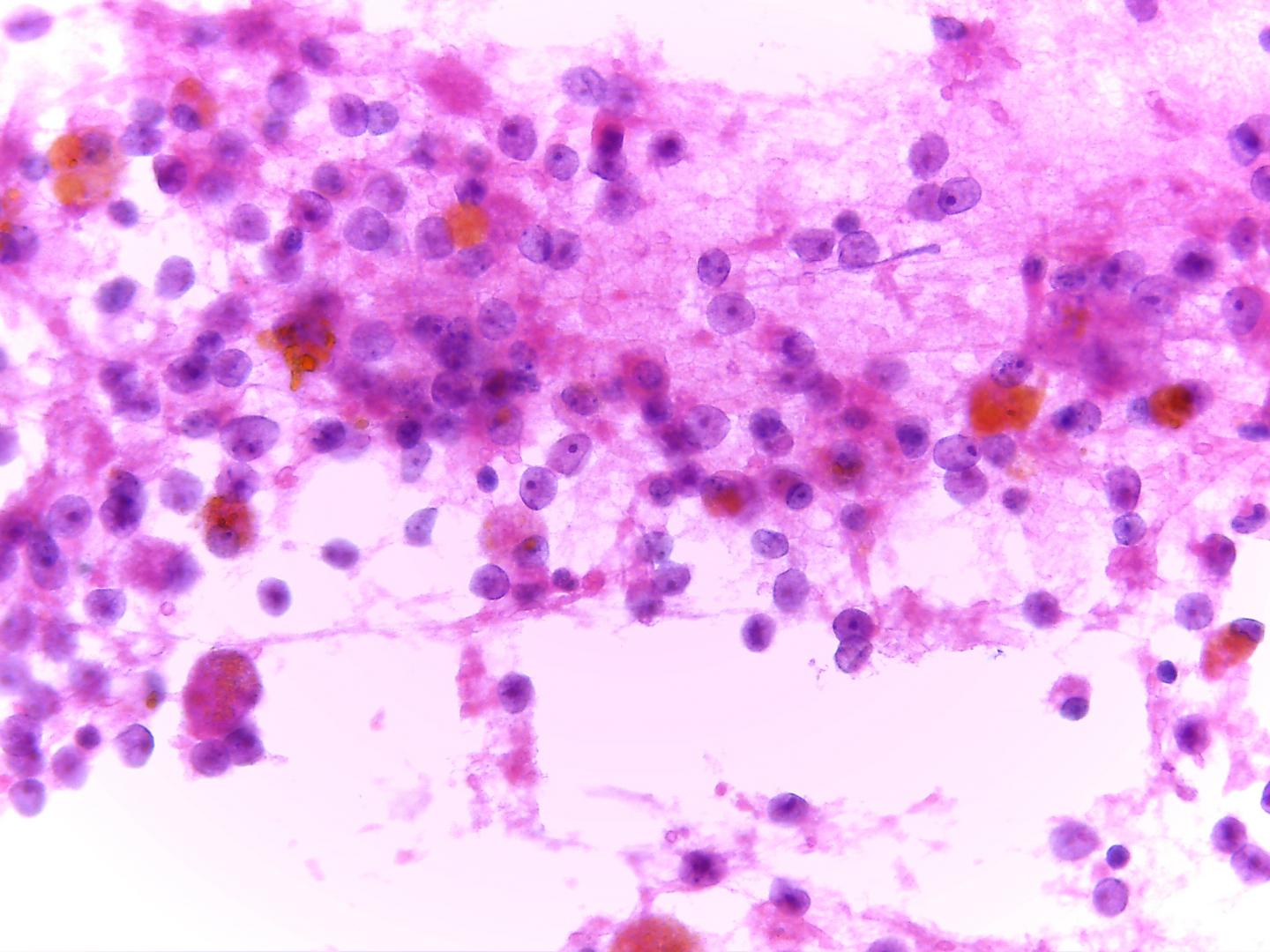
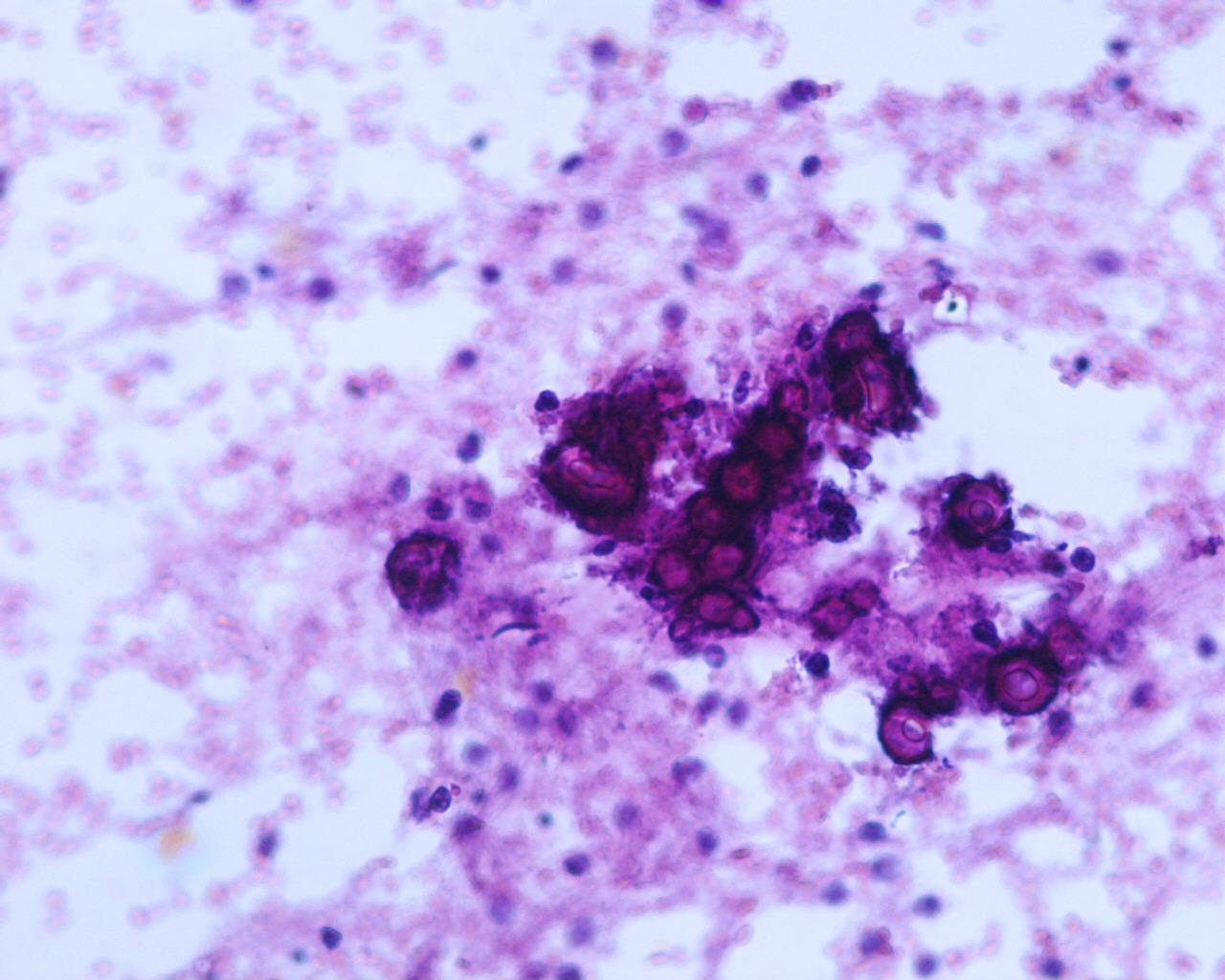
Fig 10 a – Renal cell carcinoma- abundant clear micro vacuolated cytoplasm with ill-defined borders and macrophages with hemosiderin pigment,
- Clear cell RCC
- Flat sheets and trabecular, papillary aggregated tumour cells mixed with stromal components and capillaries
- Numerous single cells
- Cells with central or eccentric round nuclei
- Prominent nucleoli in high-grade tumours
- Intranuclear vacuoles common
- Pale, vacuolated or granular cytoplasm
- Cytoplasmic fragility with ill-defined borders
- High nuclear grade frequent
- Background with blood and necrosis is frequent
- Magenta-staining basement membrane-like material
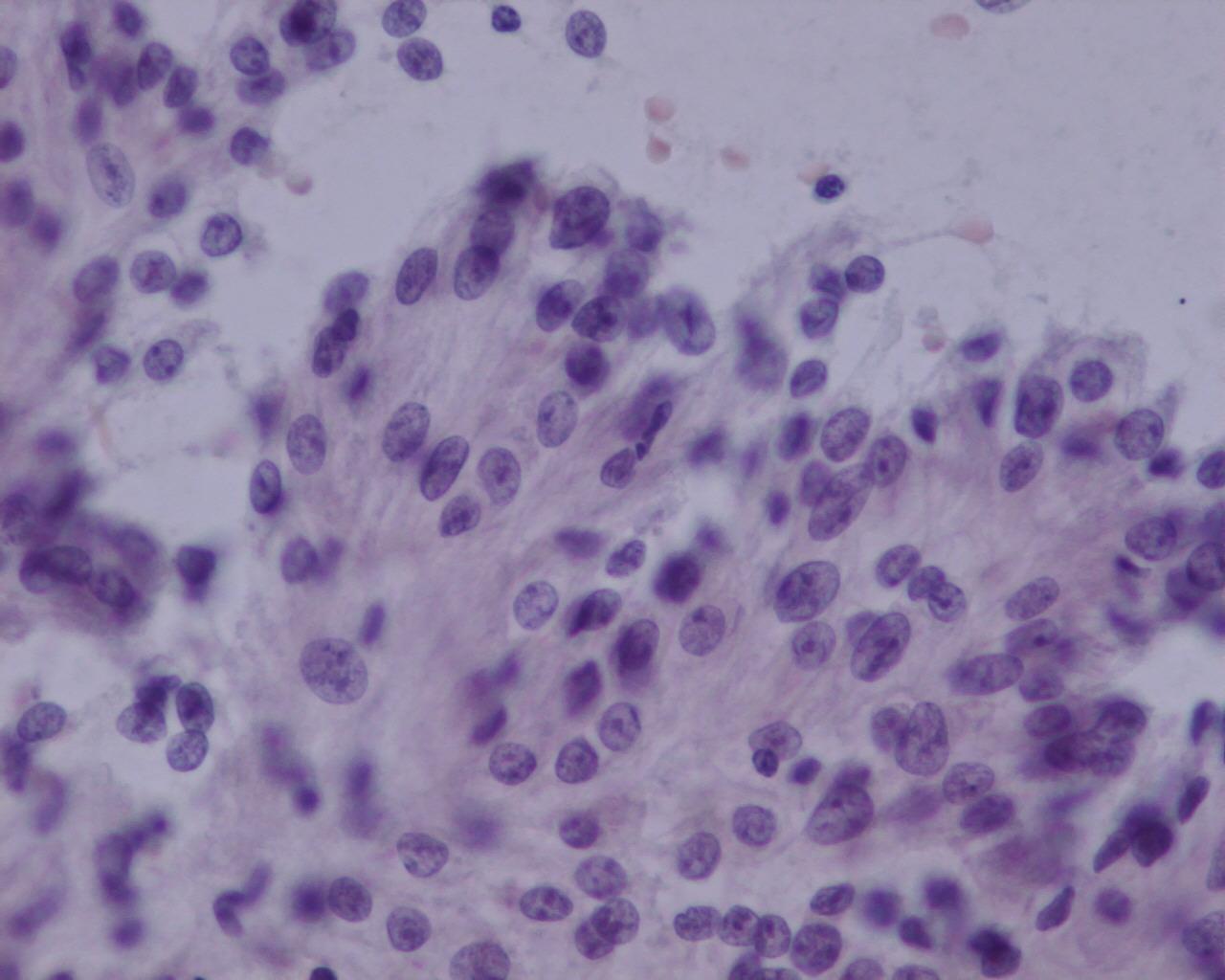
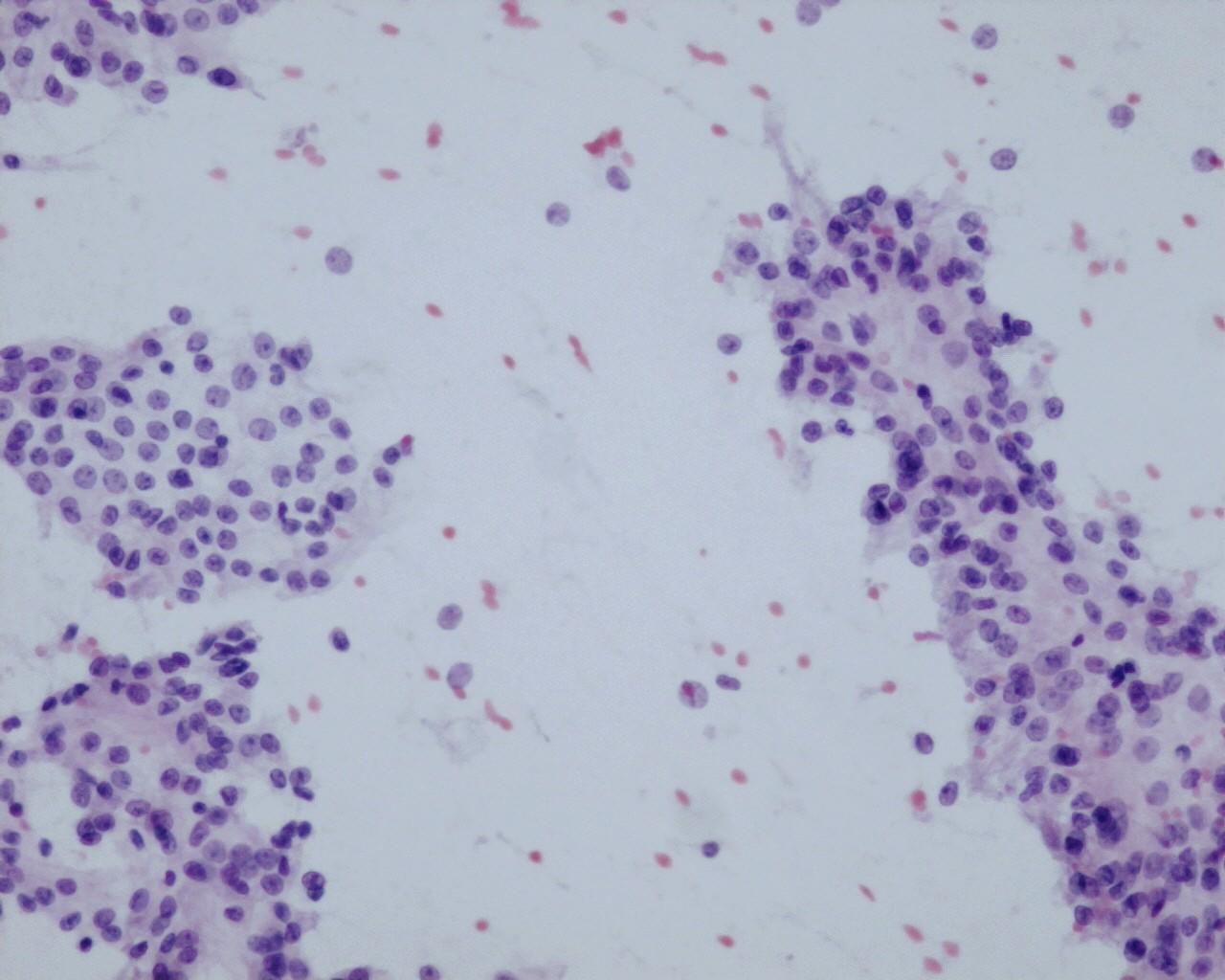
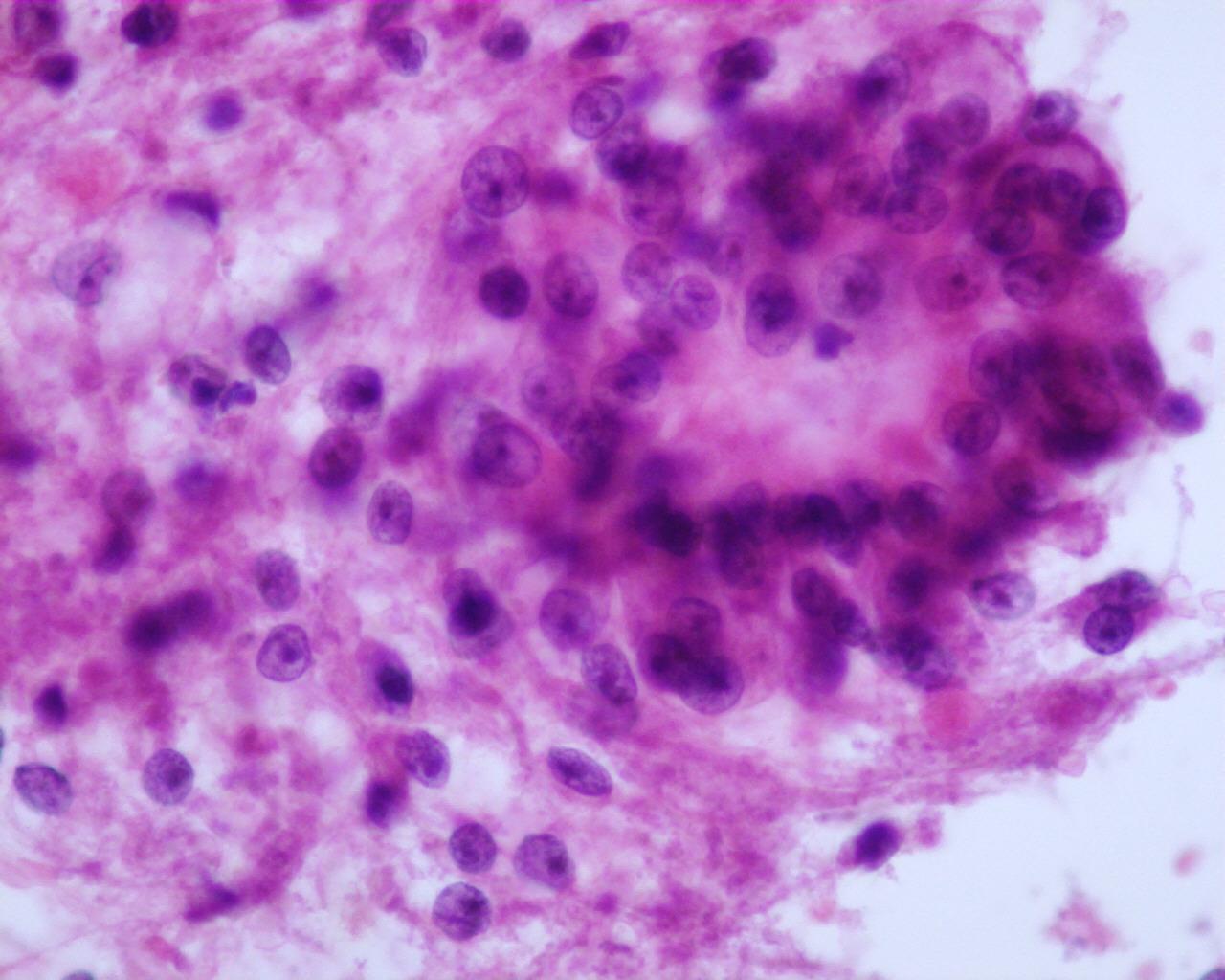
- RCC in children, Xp11.2 associated tumours
- Large polygonal eosinophilic or clear neoplastic cells
- Prominent nucleoli
- Intracytoplasmic hyaline bodies and intranuclear inclusions
- Papillary pattern more frequent
- Psammoma bodies are frequent
- t (6;11) (p21;q12)-No reports on cytological features have been described.
Immunocytochemistry
- Clear cell RCC:
- RCC: positive
- AE11AE3: positive
- Vimentin: positive
- Pax8: positive
- EMA: positive
- CD10: positive
- Ck7: negative
- AMACR: negative
- Alpha-inhibin: negative
- Melan A: negative
- Xp11.2 RCC associated tumours:
- Renal cell carcinoma marker antigen: positive
- CD10: positive
- EMA: positive (focal)
- Vimentin: positive (focal)
- TFE3: positive ( nuclear labelling)
- AE1AE3: usually negative
- S-100 protein, desmin: negative
- t(6;11)-related RCC:
- HMB45: positive
- Melan A: positive
- Cytokeratin’s: negative
Genetic studies
Contrary to what is observed in adults, childhood RCC is less frequently associated with mutations and deletion of the VHL genes
- Xp11.2 associated tumours
- t(X;1)(p11.2;q21)-fusion TFE3 gene with PRCC gene
- t(X;1)(p11.2;p34)-fusion TFE3 gene with the NonO(p54 nrb)
- t(X;17) (p11.2;q25)-Balanced translocation that fuses TFE3 gene with the ASPL gene-(same translocation of alveolar soft part sarcoma, in this last tumour it is unbalanced translocation is present).
- t(6;11)-associated RCC
- t(6;11)(p21;q12)
Differential diagnosis
- Adrenal cortical cell tumours
- Some cases are indistinguishable by histological means alone
- Alpha-inhibin: positive
- Melan A: positive
- Vimentin: positive
- EMA: negative
- RCC: negative
- Hepatic cells
- Can be confused with granular cells in clear cell RCC
- Better defined cytoplasmic borders
- Cytoplasmic iron
- Hep-par 1:positive
- Arginase :positive
Main points
- Xp11.2-associated tumours comprise a significant percentage of all renal carcinomas in children
- Renal cell carcinomas are rare in childhood and comprise less than 5% of paediatric renal tumours
- Cases of renal cell carcinoma arising in Wilms’ tumours have been described
- Association with Von-Hippel-Lindau syndrome is less frequent in childhood