Clinical features
- More frequent non rhabdomyosarcoma soft-tissue sarcoma in childhood
- Deep seated tumour, arising from major nerves or pré existent neurofibroma
- Median age of 10 years. Congenital cases have been reported
- These tumours can recapitulate any or all elements of the nerve sheath (Schwann cells, perineural fibroblasts, fibroblasts)
- Extremities (lower leg, buttock ), trunk and the head and neck,
- 50% are associated with neurofibromatosis Type I
- 2% of patients with neurofibromatosis Type I will develop one in their lifetime
- Rarely arise from ganglioneuromas, pheochromocytomas and schwannomas
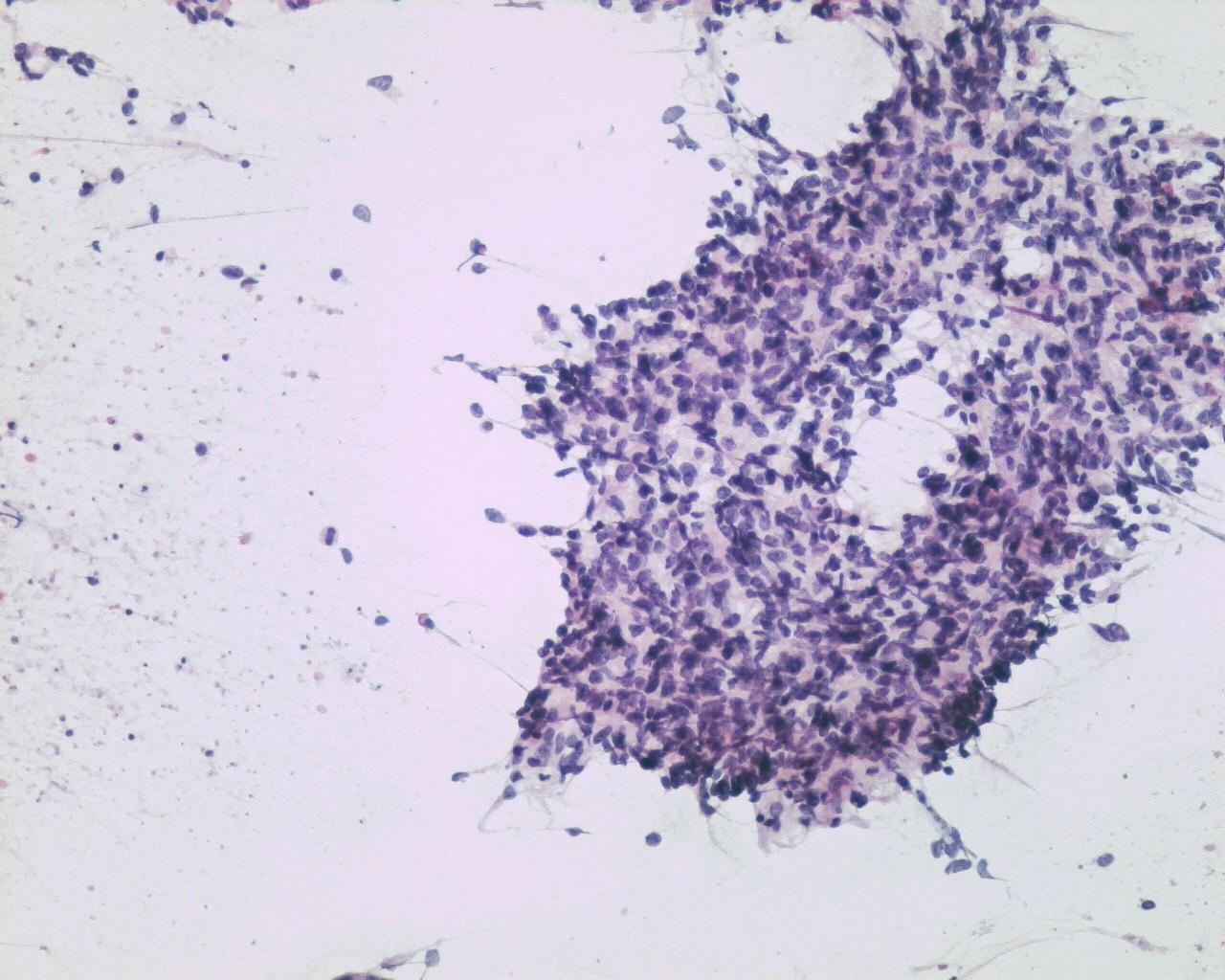
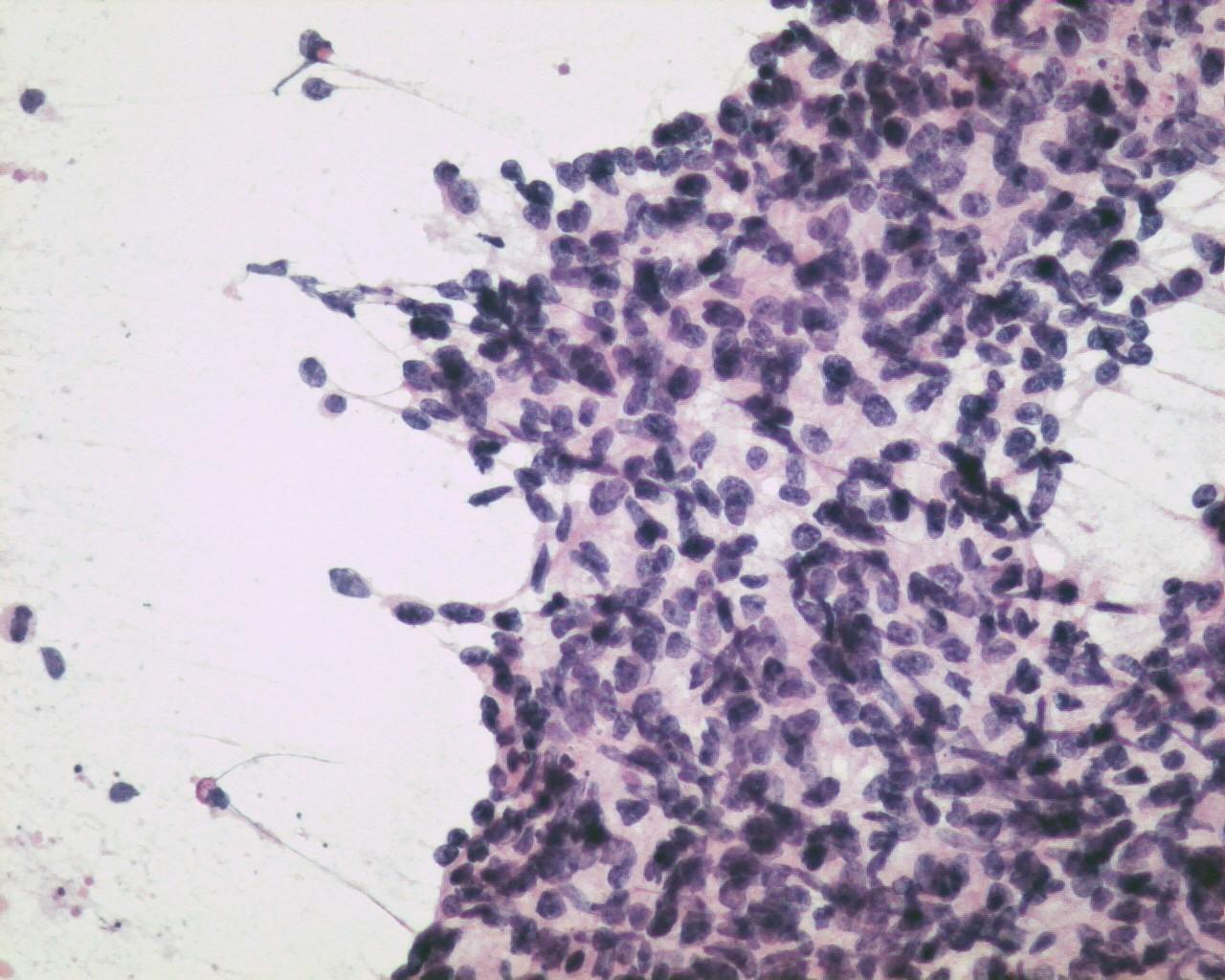
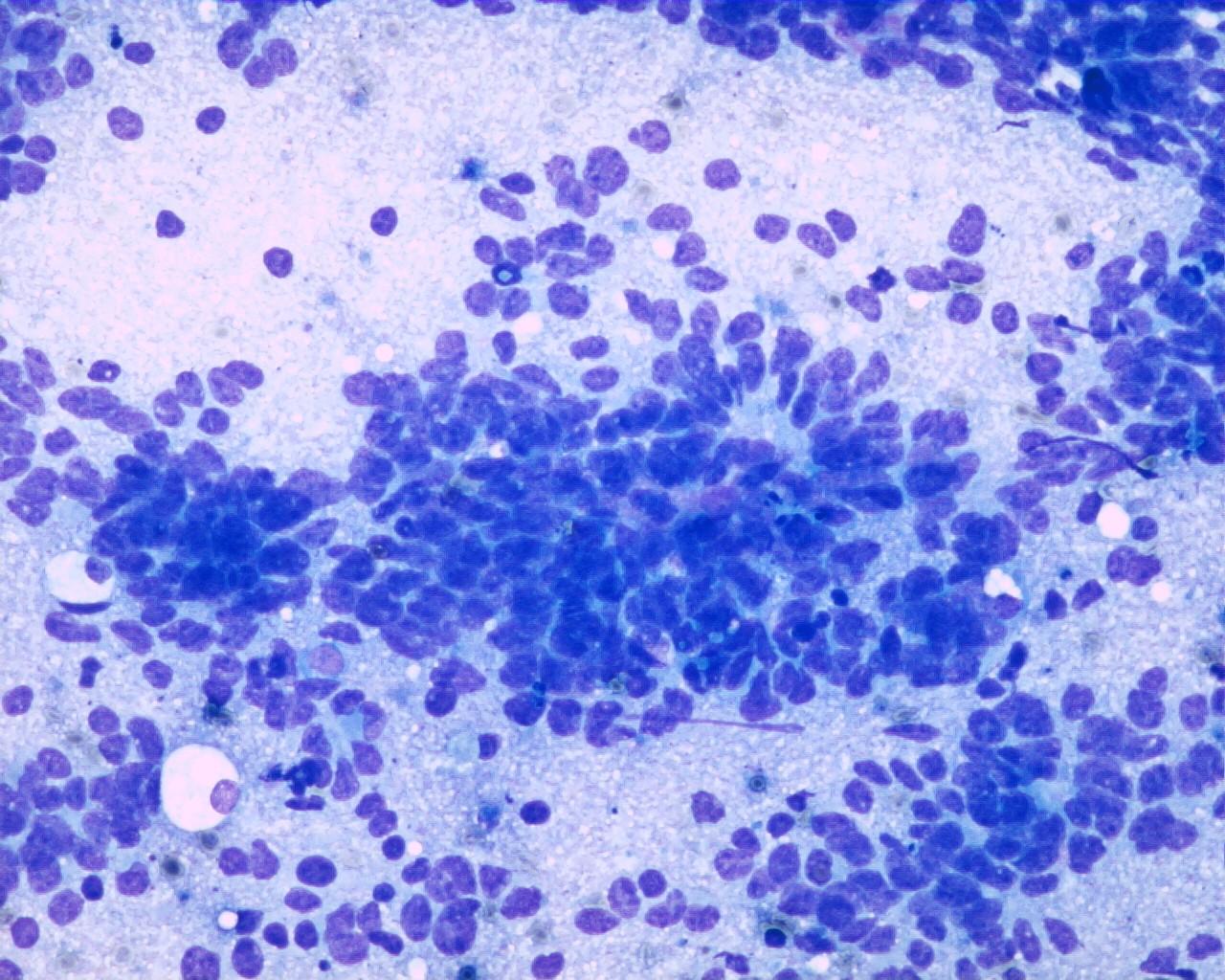
Fig 33a – Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor –Cohesive tissue fragment showing an epithelioid-like pattern area (H&E)
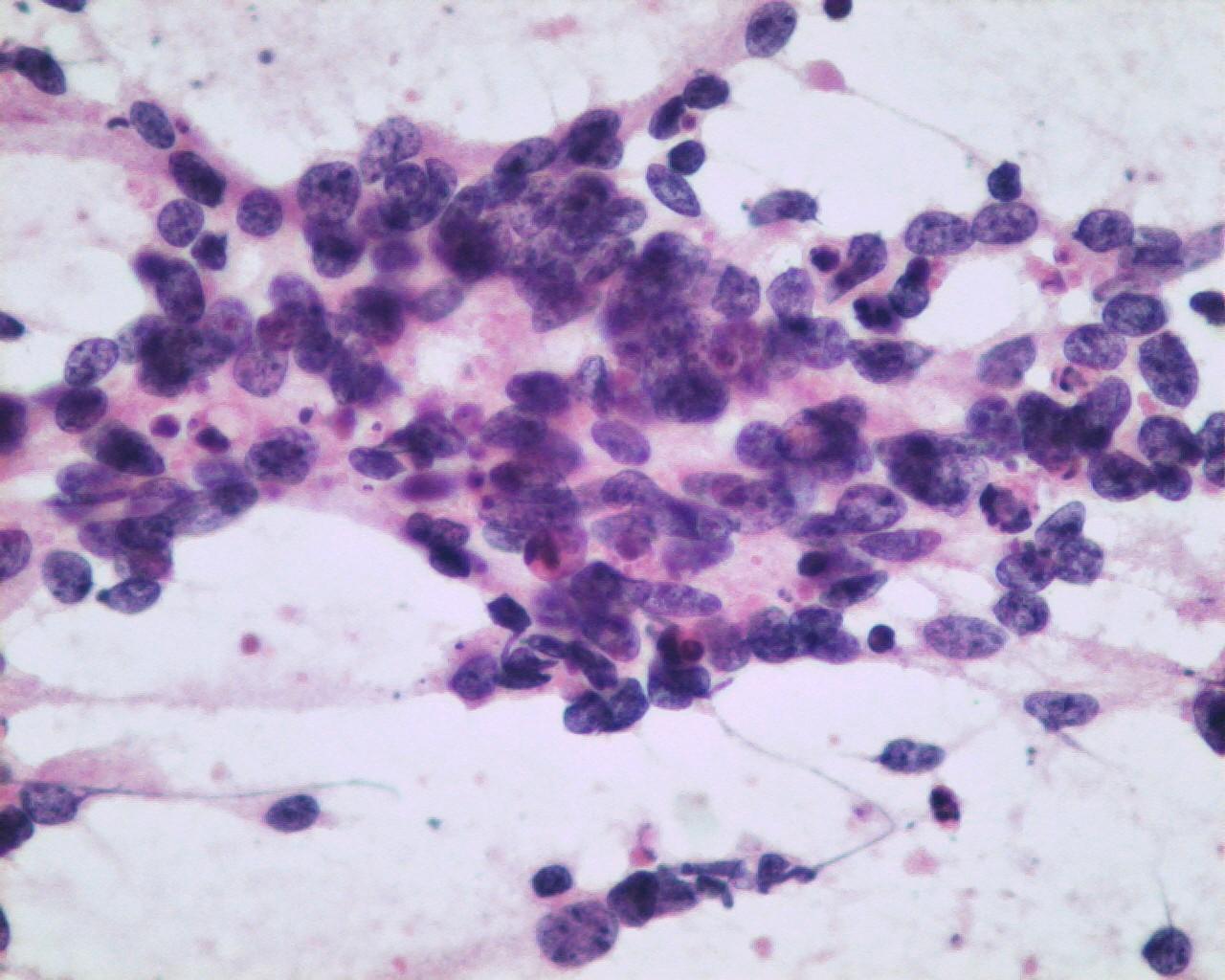
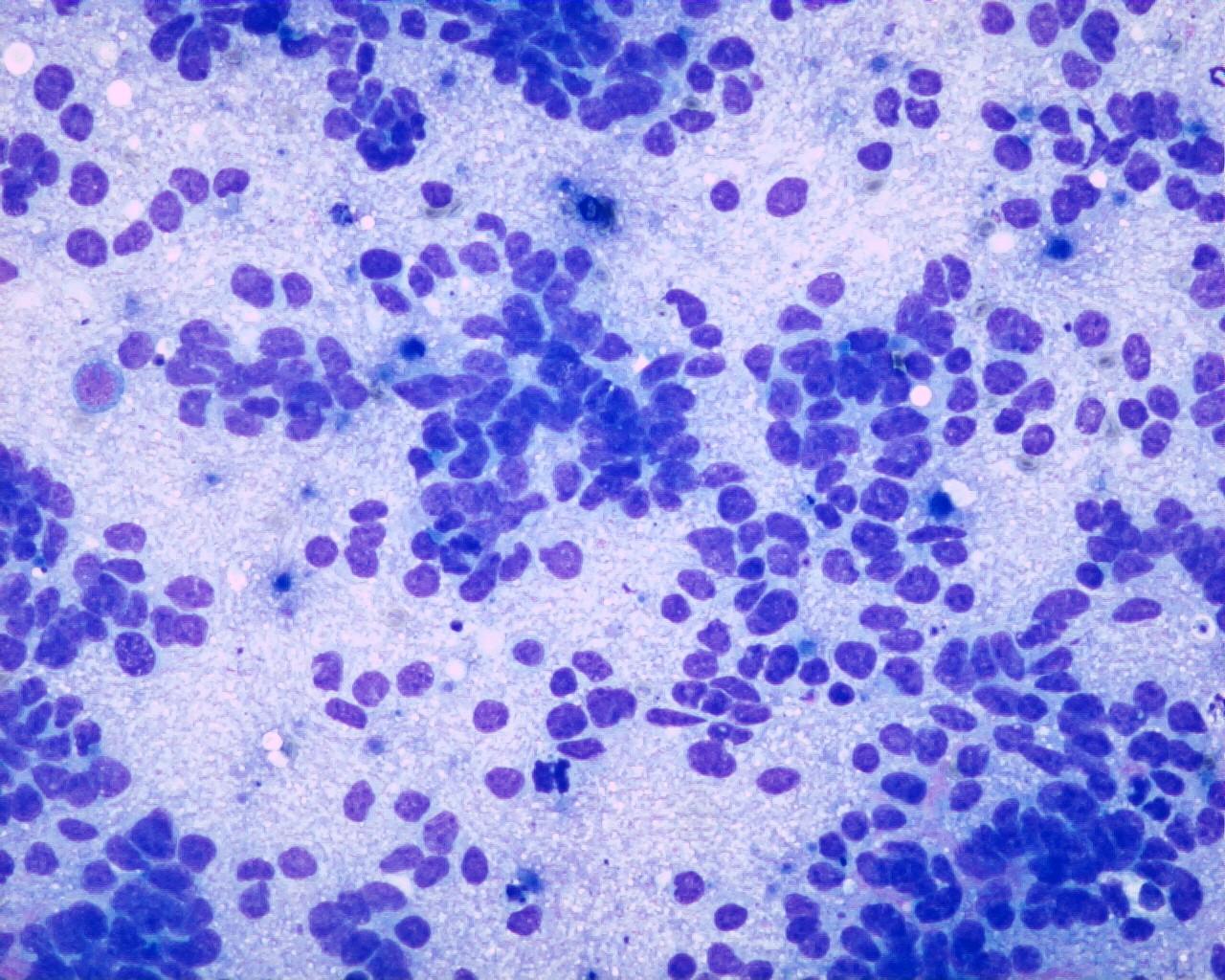
- Smears with moderate to high cellularity
- Large quantity of dissociated spindle cells
- High nuclear/cytoplasmic ratio
- Wavy nuclei
- Prominent nucleoli
- Low grade lesions are bland and monotonous-(differential diagnosis with benign lesions)
- Multinucleate anaplastic cells are common
- Myxoid or fibrillary background
- Frequent mitosis
- Pleomorphism can be present even though it is not per se a sigh of malignancy
- Rosettes or an neuroepithelial pattern can be present
Immunocytochemistry
- S100 protein: Positive (62%)
- CD57 (leu7): Positive (55%)
- CD99: Positive (86%)
- Glial fibrillary acidic protein(GFAP): Positive (cases with perineurial differentiation)
- Protein gene product 9.5 (PGP9.5): Positive (not specific)
- P53 : Positive in high grade lesions
- Desmin: Positive (Triton)
- EMA: Negative (generally)
- Keratins: Positivity is rarely described (except for keratin 7 or 19)
Electron microscopy
- Cells with slender elongated apposed cell processes
- Primitive cell junctions
- Enfolding of cell membrane with lamellar configuration
- Discontinuous basal lamina
- Round to oval nucleus with smooth contours
- Prominent nucleoli
Genetic studies
- Translocation (17;22)
- MDM2 amplification
Differential Diagnosis
- Synovial sarcoma
- Biphasic pattern
- keratins( 7,or 19): Positive
- Cellular schwannomas
- Aggregates instead of loose cells
- More monomorphic cellular population
- Rare mitosis or necrosis
- Fibrosarcoma
- S-100 protein: positive (focal)
Main points
- Poor prognosis
- Metastases involve lungs, liver and bone
- Propensity to spread along the nerve
- Cases associated with Neurofibromatosis have worse prognosis