Clinical features
- Usually occurs between 6-10 years of age
- Presentation: abdominal mass, fever and pain
- Serum alpha-fetoprotein levels are normal
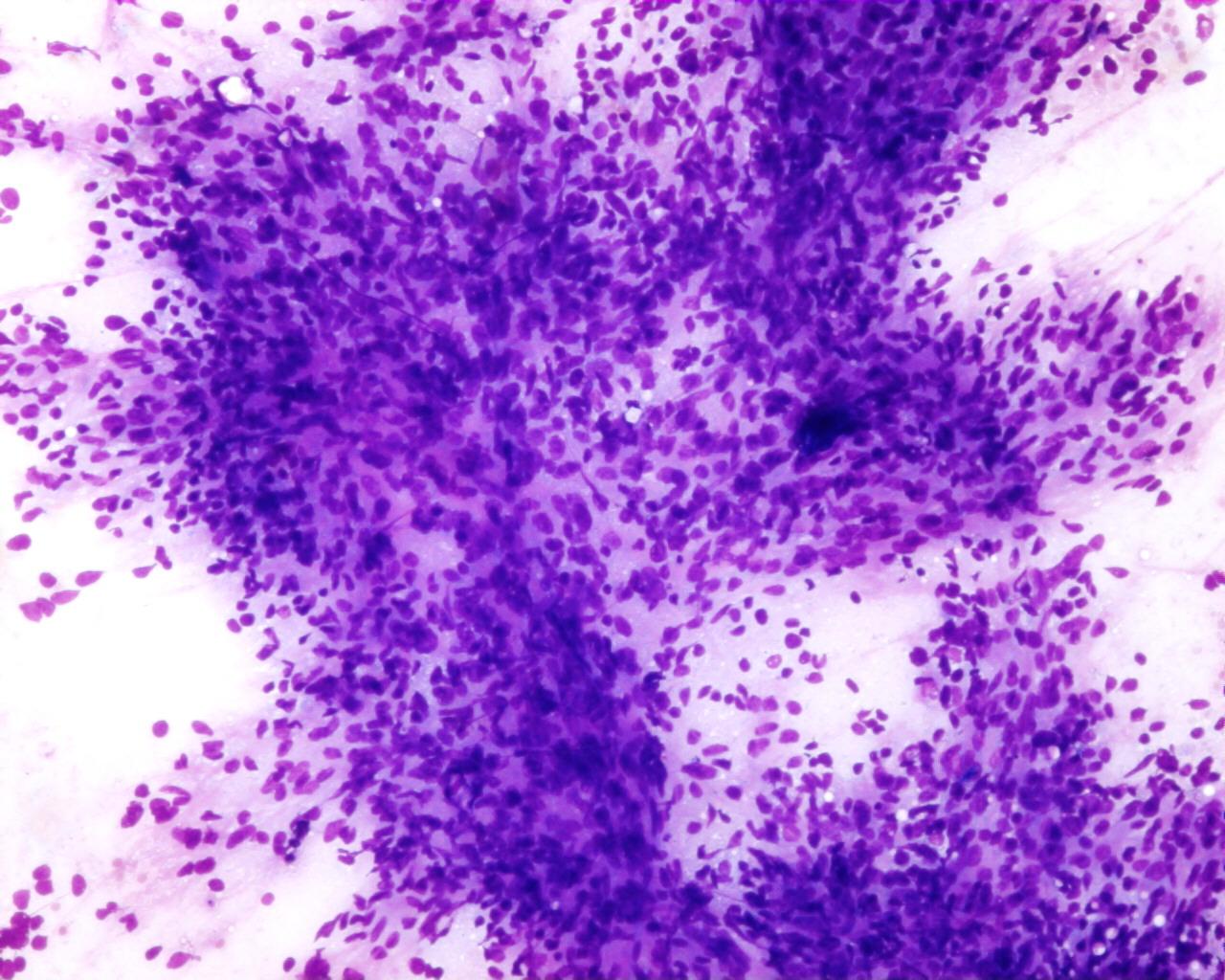
Fig 80 – Embryonal Sarcoma- Cellular smear with mesenchymal clusters in a myxoid matrix (Giemsa)
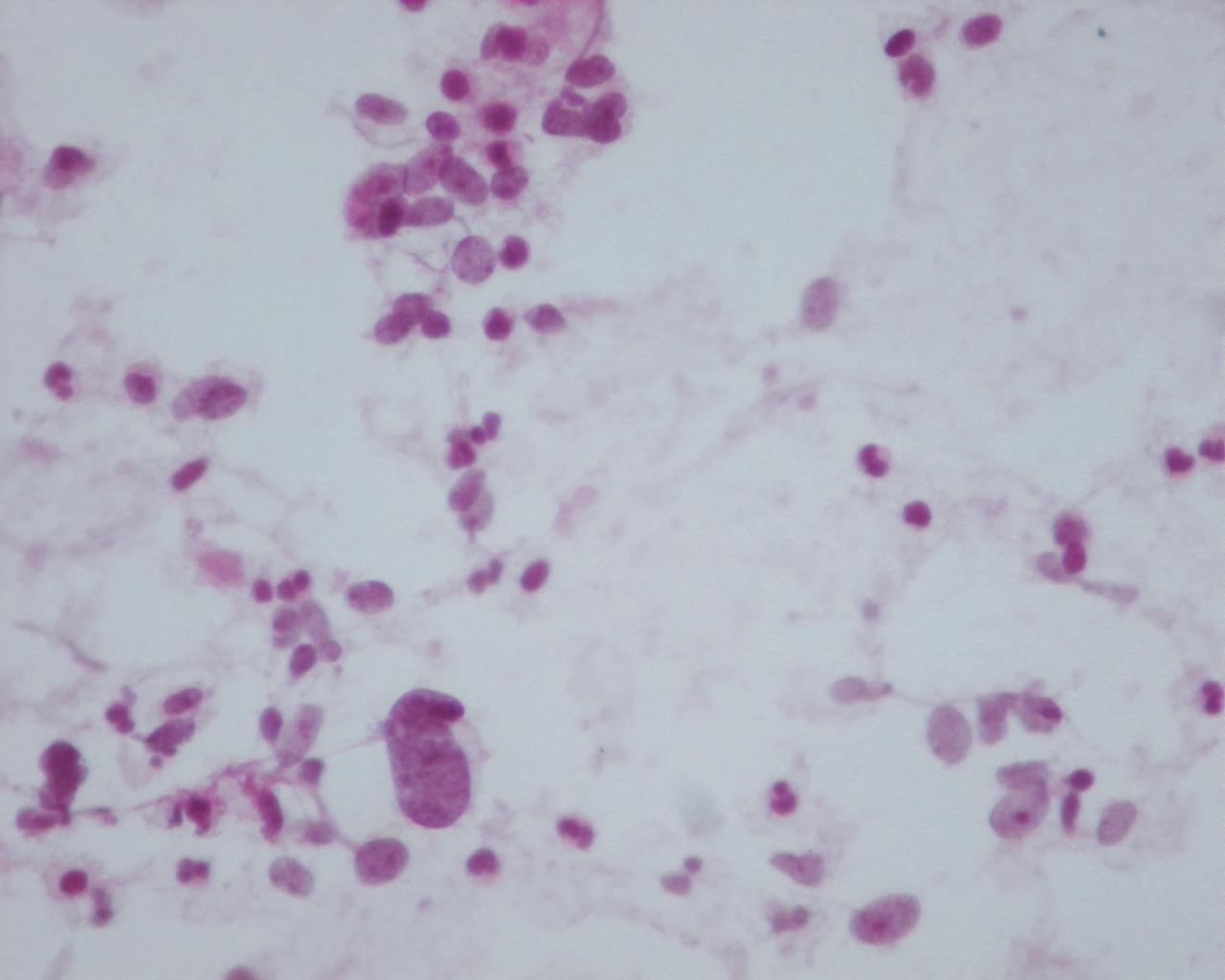
- Cellular smears
- Mesenchymal clusters
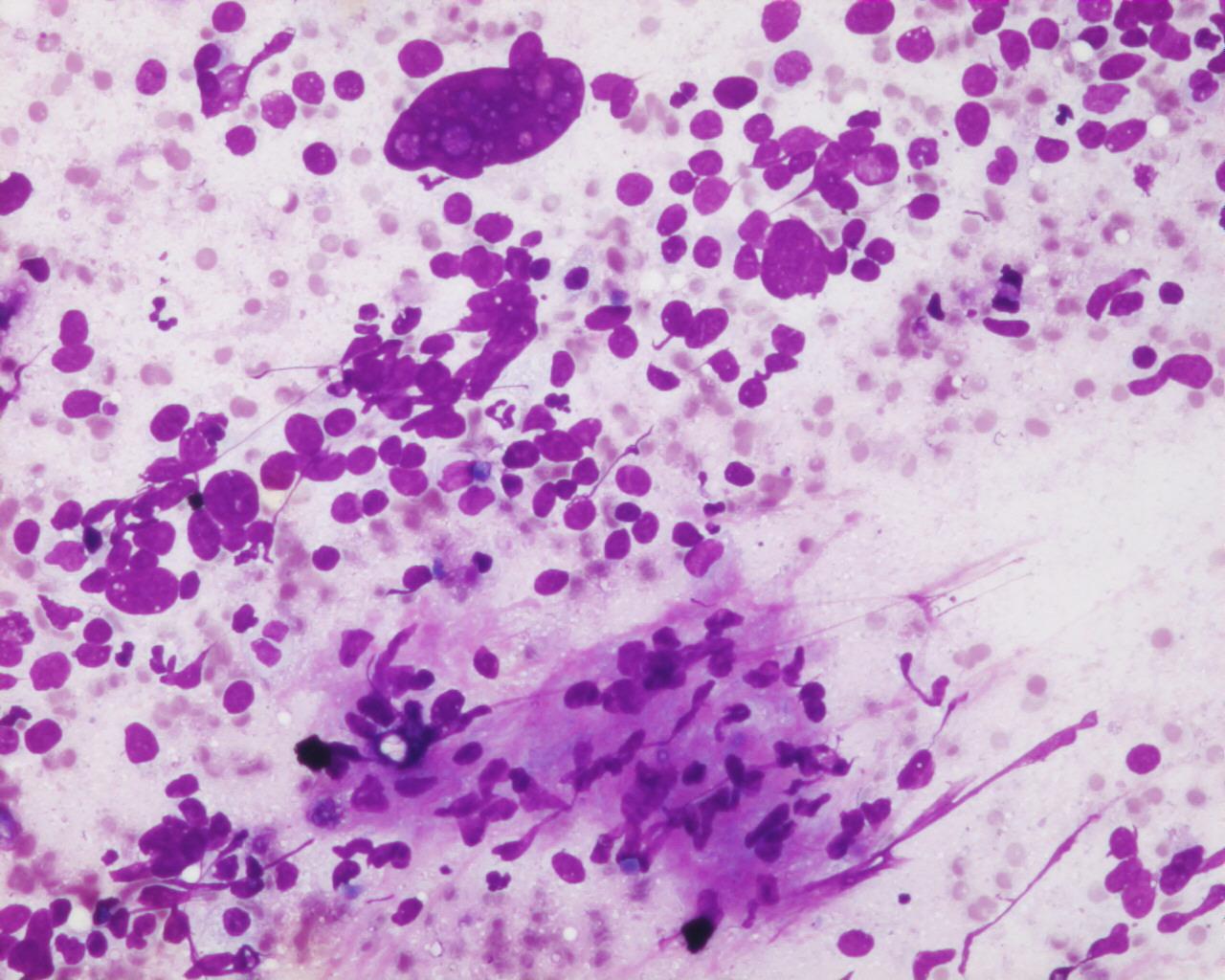
- Heterogeneous population of tumour cells (spindle, oval, pleomorphic and multinucleated giant cells)
- Moderate amount of cytoplasm with poorly defined limits
- Nuclei with coarse chromatin
- Myxoid background
- Hyaline globules in the background or intracytoplasmic
- Haemorrhage and necrosis
Immunocytochemistry
- Anti-chymotrypsin: positive
- Alpha-1-antitrypsin: positive
- Desmin: variable
- Muscle-specific actin: variable
- Vimentin: variable
- Alpha-fetoprotein: negative (hyaline globules)
- Myogenin: negative
Genetic studies
Rearrangements of chromosomal band 19q13.4,
t (11; 19) (q13; q13.4)
Differential diagnosis
- Mesenchymal hamartoma
- In patients under one year of age
- Bland tumour cells
- No cellular pleomorphism
- Embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma
- No hyaline globules
- Rhabdomyoblastic differentiation
- Myogenin : positive
- Hepatoblastoma (mixed and embryonal)
- Lack of myxoid stroma
- Lack of cellular pleomorphism
- Lack of hyaline globules
- Presence of extra medullary haematopoiesis
Main points
- Occasionally arising in mesenchymal hamartoma,
- Primitive mesenchymal neoplasm
- Treatment: complete surgical resection
- Death within two years due to direct extension
- Metastasis to lung and bone