Clinical features
- Children and young adult
- Usually in males
- Abdominal pain
- Abdominal location with predilection for pelvic region, as solitary or multiple nodules
- ascites is a constant feature
- Cases have been described in lungs, pleura, ovaries, pancreas, testes, cranial fossa, parotid, and soft tissues
- Lymph node metastases are rare
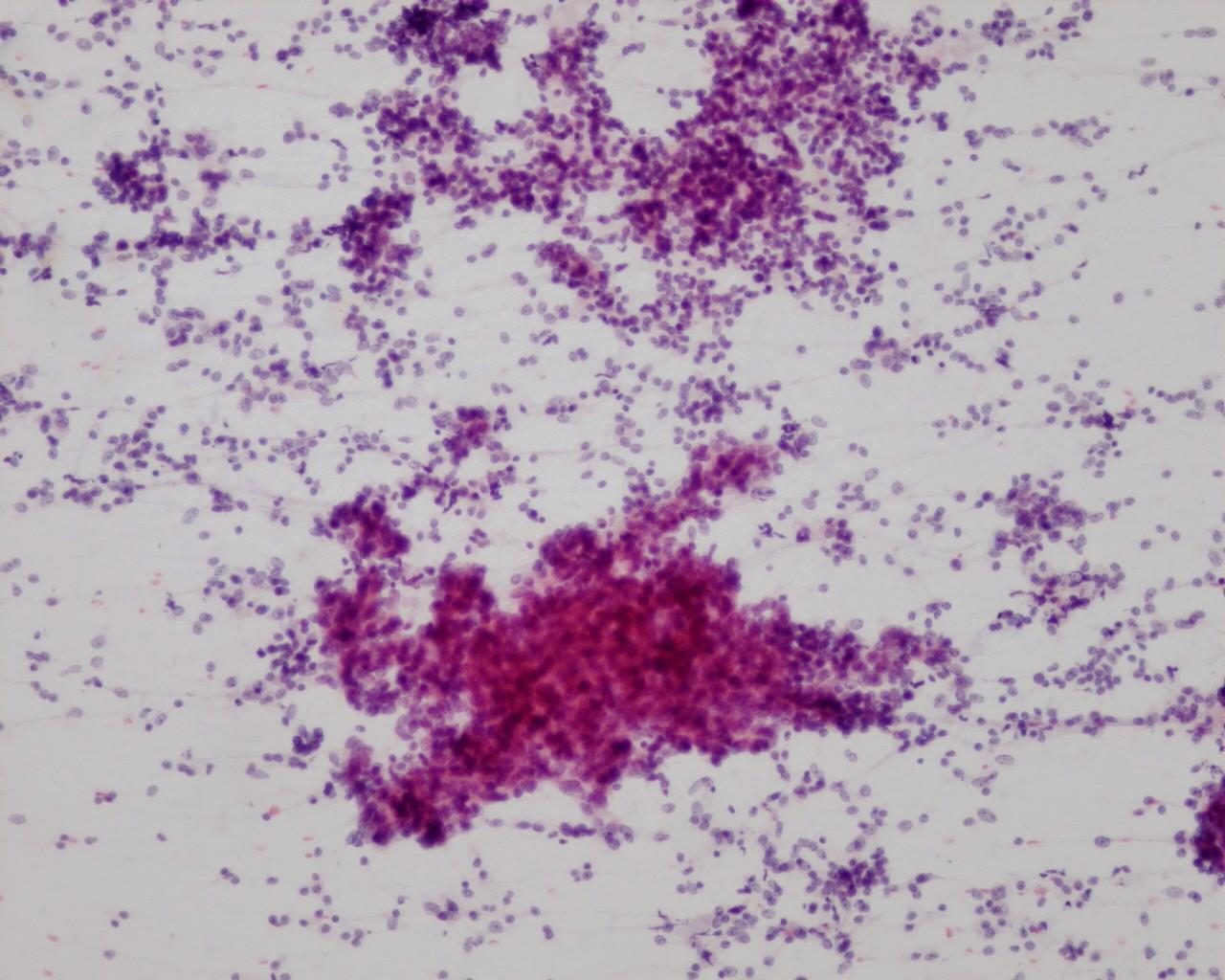
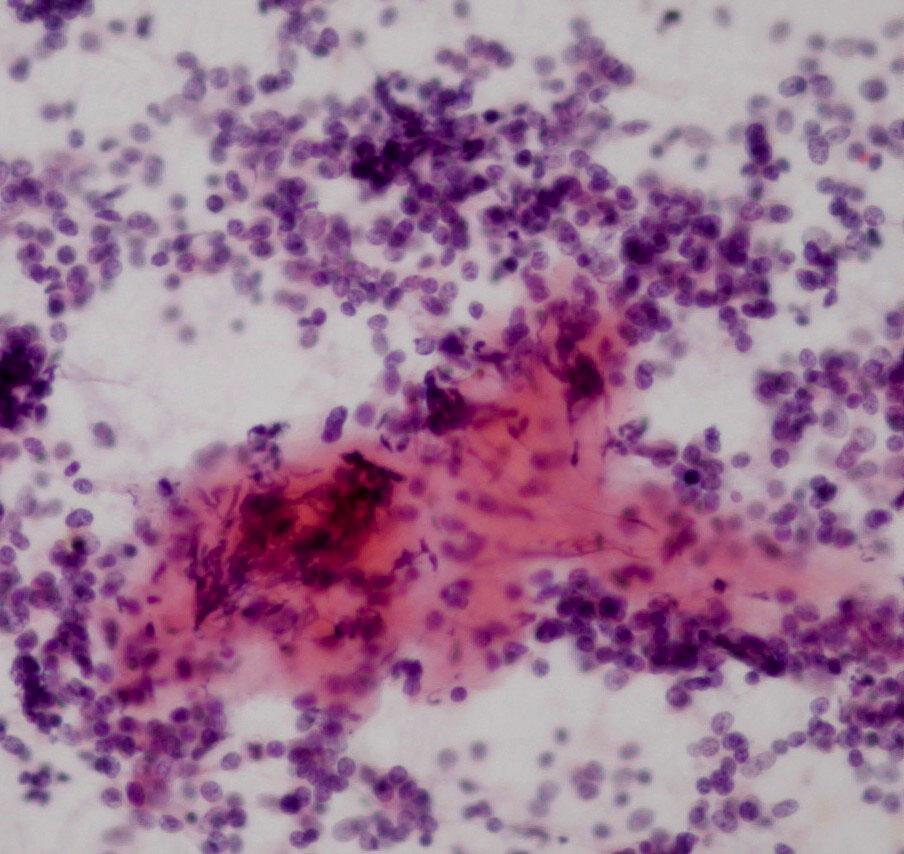
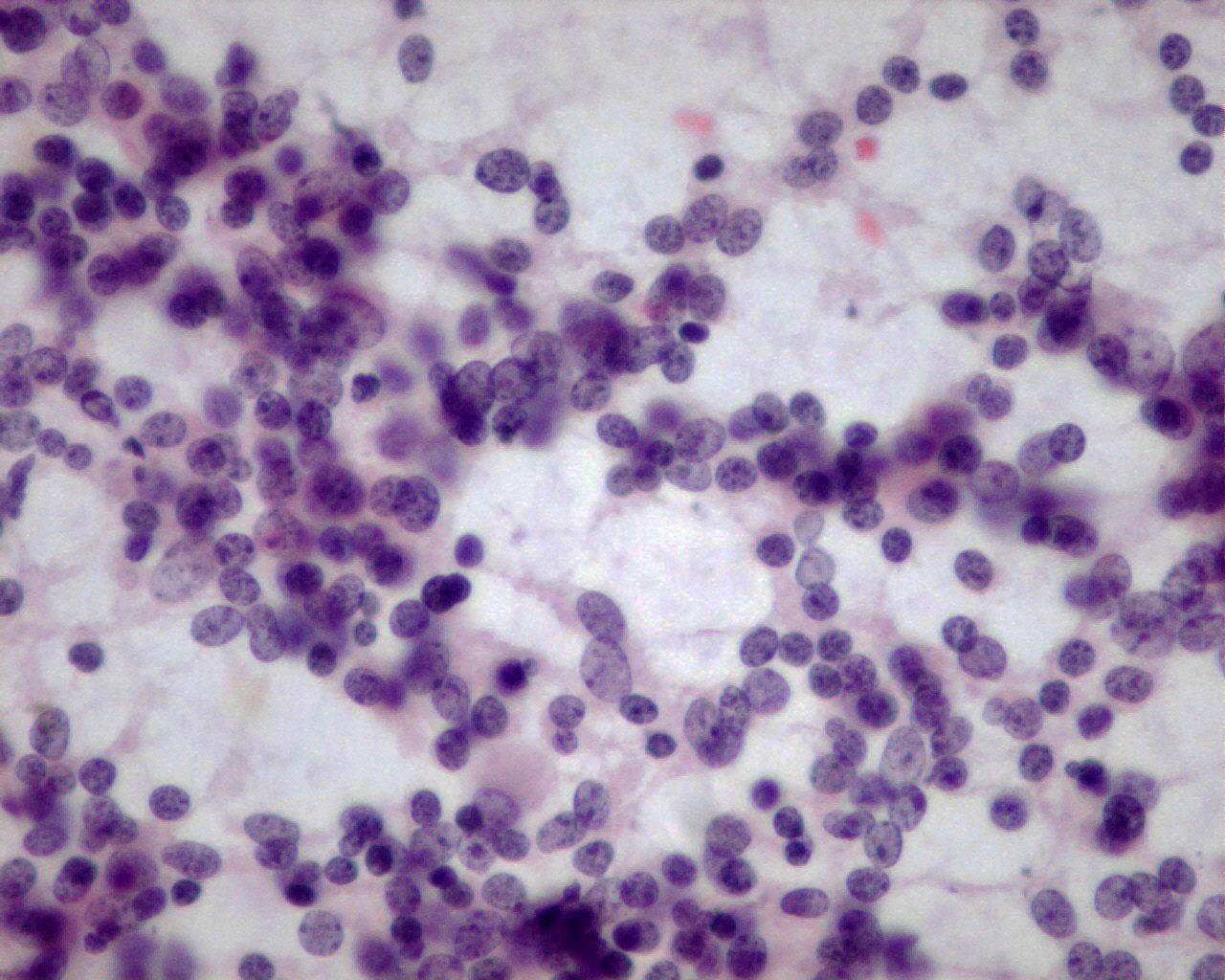
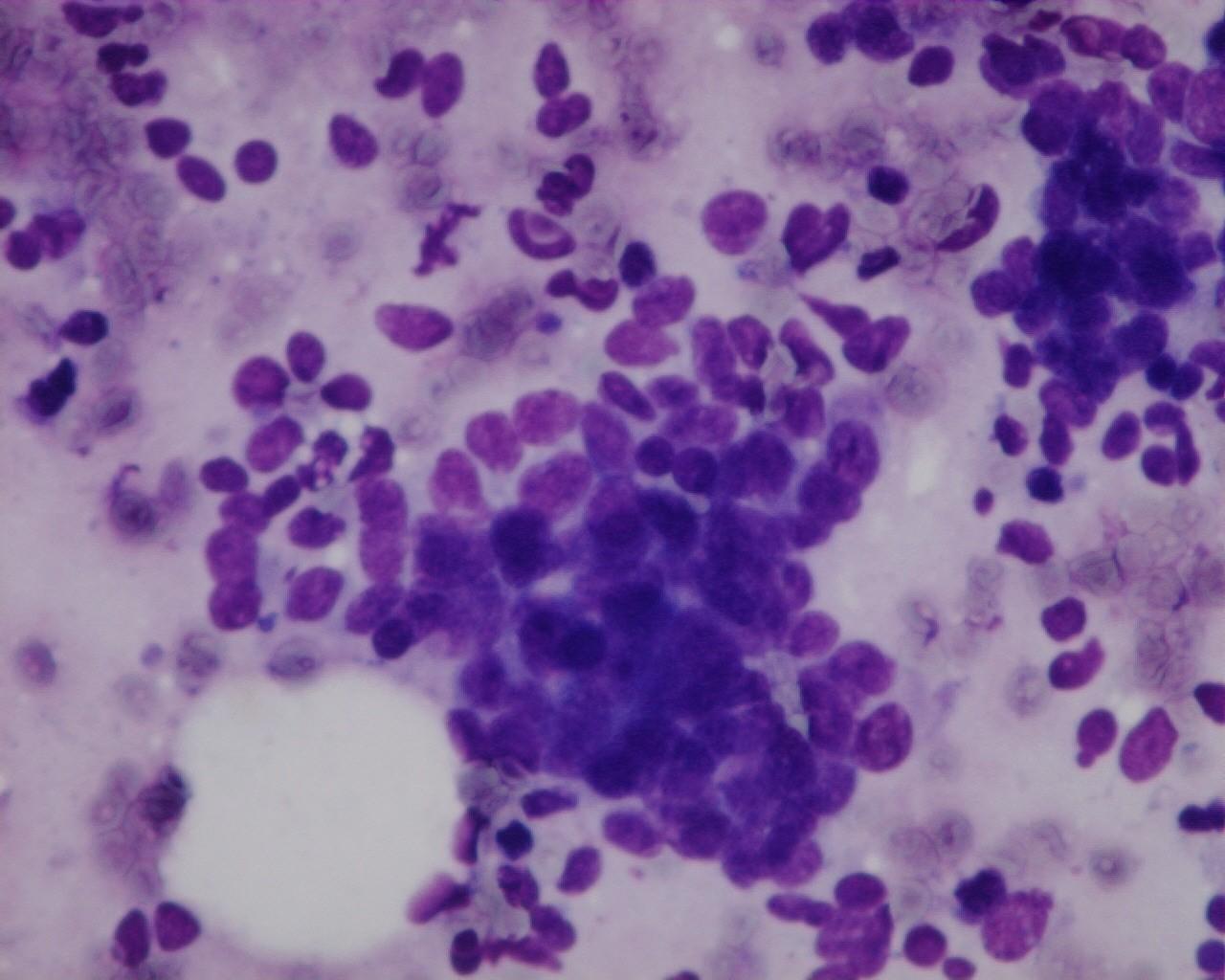
Fig 54 – Desmoplastic small cell tumor –Single and three dimensional groups of monomorphic small round cells (H&E)
- Single and clusters (sheets or three-dimensional groups) of monomorphic small round cells
- Neoplastic cells with uniform nuclei
- Nuclear moulding
- Fine granular chromatin
- Inconspicuous nucleoli
- Sparse cytoplasm
- Stromal fragments
- Other patterns: rhabdoid, signet ring or rosettes
Immunocytochemistry
- Coexpression of desmin (dot), EMA, AE1AE3, CAM5.2 or Vimentin
- NSE: positive
- Myo-D1: negative
- Smooth muscle actin: negative
- WT1: positive
- CD99: membranous staining negative (35% positive reported by Gerald and et al, but only cytoplasmic)
- Chromogranin: negative
Genetic studies
- t(11;22)(p13;q12)
Differential diagnosis
- PNET
- Desmoplastic stroma: in the classical type is absent
- Intracytoplasmic glycogen
- CD99: typically positive (membranous)
- FlI1: positive
- Cytokeratin and EMA: positive
- Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma
- Nuclear moulding is not a feature
- Tigroid background (Giemsa stains)
- Smooth muscle actin and Myo-D1: positive
- Myogenin: positive
- Neuroblastoma
- Younger children
- Neuropil
- Frequent rosettes
- Other small round cell tumours, depending on the site of origin: pancreatoblastoma, pancreatic neuroendocrine tumours , hepatoblastoma and Wilms’ tumour
Main points
- Some authors advent a probable origin from a primitive mesothelial cell-“Mesothelioblastoma”, based on the immunoexpression to desmin, WT1, vimentin and cytokeratin’s, by both mesothelium and this entity
- Extremely aggressive neoplasm: average survival less than three years
- Weak response to chemotherapy