This content is also available in:
Español
Português
Čeština
Magyar
Polski
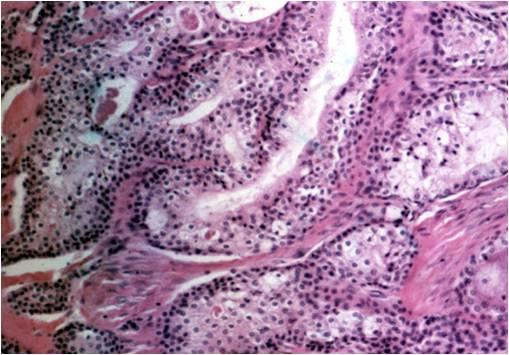
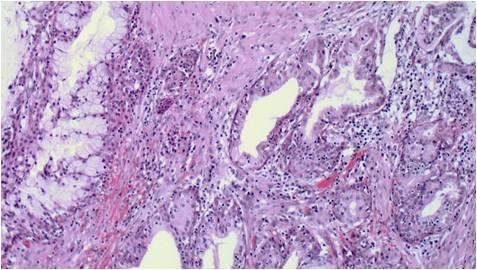
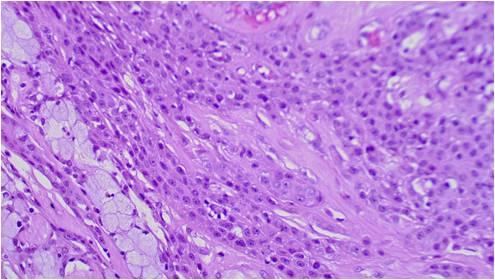
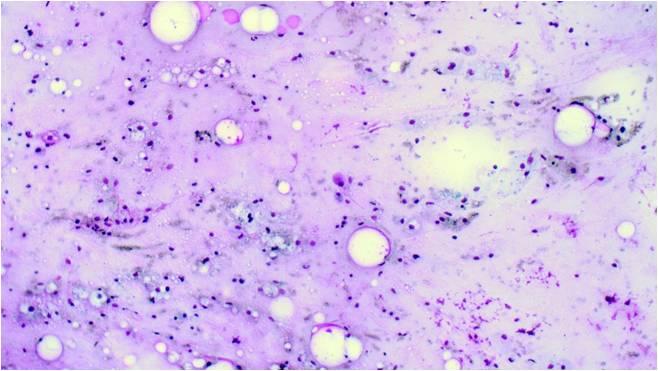
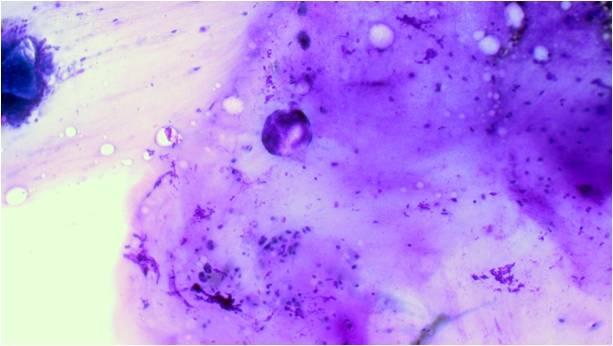
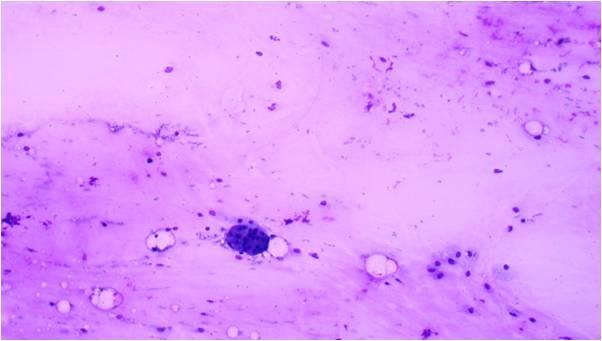
This tumor consists of squamous, mucus-producing and intermediate cells embedded in a mucinous background. It is the most common primary salivary gland malignant tumor in both children and young adults. Low, intermediate and high grade tumors are distinguished in histology on the basis of the presence of a cystic component, necrosis, neural invasion, proportion of epidermoid cells as compared to mucinous ones, anaplasia and mitotic count.
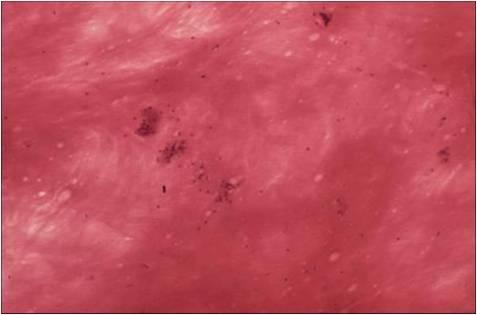
The cytological smear is sometimes very typical: all the cell types are found embedded in a mucinous background. In some cases atypia are mild, oncocyte-like epidermoid cells predominate in a dirty, ‘thick’ background, resembling a Whartin tumor. Since the mucoid material get easily into the puncturing needle even without containing epithelial cells, it is one of the most difficult cytological diagnoses in the salivary glands!