Diagnostic criteria for NHL
Chronic lymphatic leukaemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL) Incidence: 7-8% of all NHL. Cytology: Smears show monotonous, dispersed cell populations composed of small lymphocytes with clumped chromatin and occasional, small, nucleoli; mitoses are absent or rare. Accelerate phases of CLL/SLL show larger, nucleolated, cells (paraimmunoblasts) and mitoses, and should not be confused with Richters syndrome, which is […]
Metastases
Clinically evident metastatic lymph nodes are generally characterized by diffuse involvement; hence, FNC is diagnostic in most cases;when the primary tumour is unknown, FNC may contribute to its identification. As in case of lymphomas, the immediate evaluation of the smear may require additional passes, can orientate the management of the diagnostic material and lay out […]
Hodgkin Lymphoma
HODGKIN LYMPHOMA (HL) General features Classification FNC evaluation Nodular lymphocyte predominant, Hodgkin lymphoma: Cytological findings Classical Hodgkin lymphoma: Cytological findings General features HL represents approximately 30% of all lymphomas and has a bimodal age curve with a peak at 15-35 years and a second peak over forties. EB virus is probably involved in the pathogenesis, […]
Non Hodgkin lymphoma
General features NHL is a heterogeneous group of neoplasms which represent 2-3% of all tumors in the Western World. They encompass both the slowest and the fastest growing tumors, ranging from chronic lymphatic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma which, in the early stages, may be left untreated (watch and wait), to lymphoblastic lymphoma, which require timely and […]
Technical aspects
FNC and smear preparation Basic staining FNC material management and ancillary techniques Cytospin Cell block Immunocytochemistry (ICC) Flow cytometry (FC) Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) FNC and smear preparation FNC of palpable lymph nodes should be performed using a 23- or 25-gauge needle, with or without aspiration. Small lymph nodes (1 […]
Normal lymph node histology and cytology
Normal lymph node histology Lymph nodes are oval masses surrounded by a fibrous capsule and divided by septa. The internal areas are divided and supported by reticular fibers of variable thickness. The capsule is reached by afferent lymphatic ducts that carry the lymph flowing in the sub capsular sinus toward the peripheral sinus. Lymph nodes […]
Reactive lymph node
General features Non-specific hyperplasia Viral and post-vaccinial HIV infection Mononucleosis Sinus histiocytosis Suppurative lymphadenitis Granulomatous lymphadenitis Toxoplasmosis General features Lymph nodes react to different antigen stimulation with enlargement and expansion of one or all the anatomical areas. The number and sites of the lymph nodes involved as well as the entity and duration of the […]
Lymph Node
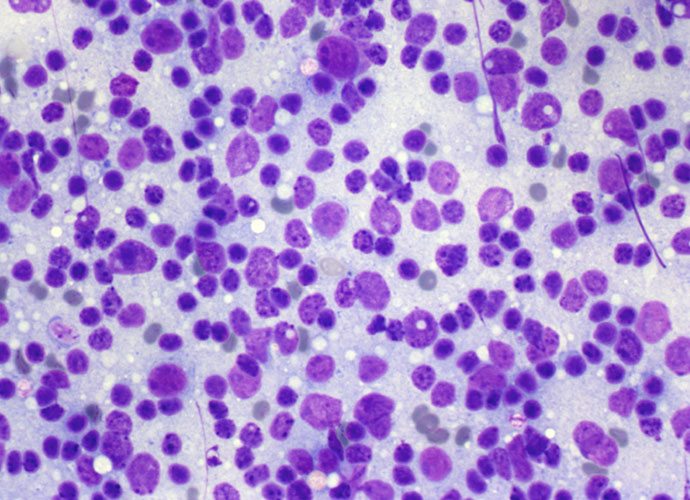
Introduction Lymph nodes were probably the first organs to be investigated by fine needle cytology (FNC) and the last in which this technique has been accepted by clinicians as a useful diagnostic procedure. Risk of seeding, false negatives, failure to discriminate between reactive hyperplasia and lymphoma, have been put forward as a limitation or useless […]

