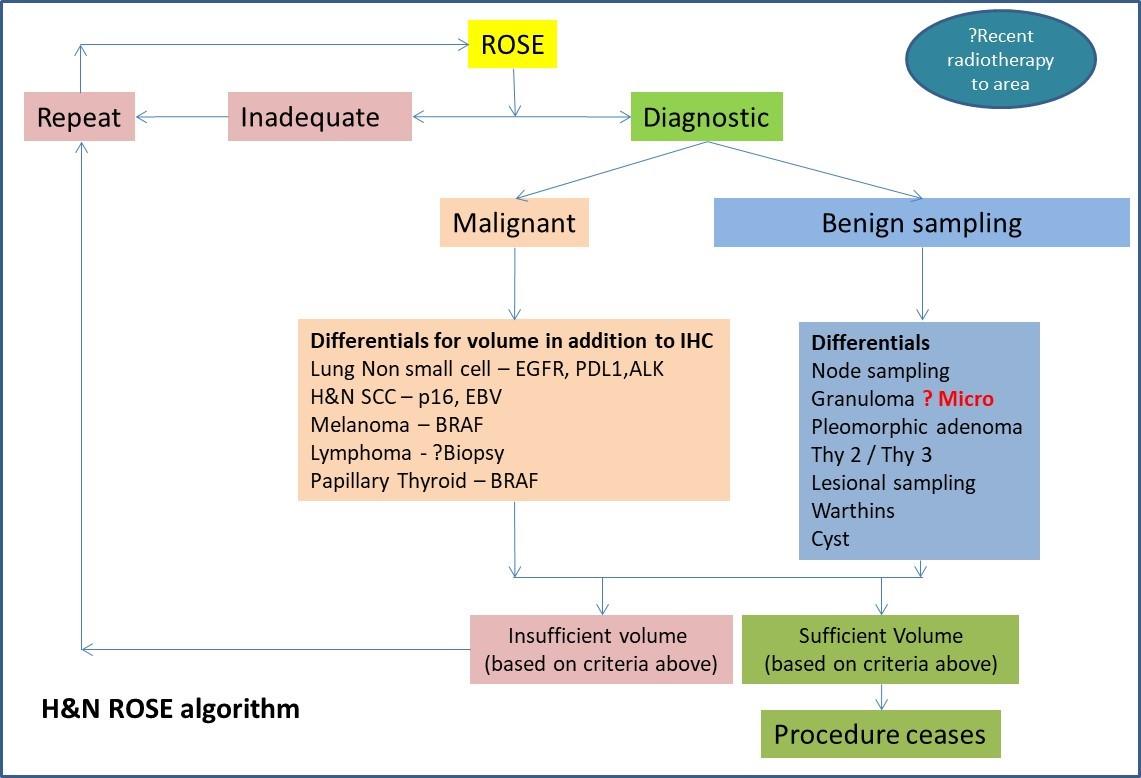
Images first published: Glinski et al. Single slide assessment: A highly effective cytological rapid on?site evaluation technique for endobronchial and endoscopic ultrasound?guided fine needle aspiration. Cytopathology 30, 164–172 (2019).
There are many personalised therapies available for advanced lung carcinomas. ROSE SAA is vital in this area to establish that the correct diagnostic cell yield is obtained.
| Tumour type | Approved tests required for targeted therapy | Yield |
| Squamous cell carcinoma | Immunocytochemistry panel PDL1 – Programmed Death Ligand 1 | PDL1 – minimum of 100 viable cells (Be careful of necrotic lesions). Caution: Ensure that atypical single cells are not present within the necrotic debris |
| Adenocarcinoma | Immunocytochemistry panel PDL1 – Programmed Death Ligand 1 EGFR – Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor ALK – Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase ROS 1 – c-ros oncogene 1 | Approximately 50% Tumour load to ensure there is enough yield for EGFR (Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor) and ALK (Tyrosine Kinase receptor) testing. In accordance with referral centre protocol PDL1 – minimum of 100 viable cells (Be careful of necrotic lesions) |
| Small cell carcinoma | Immunocytochemistry | Local ICC requirements – dependant on panels used |
| Carcinoid | Immunocytochemistry | Local ICC requirements – dependant on panels used |
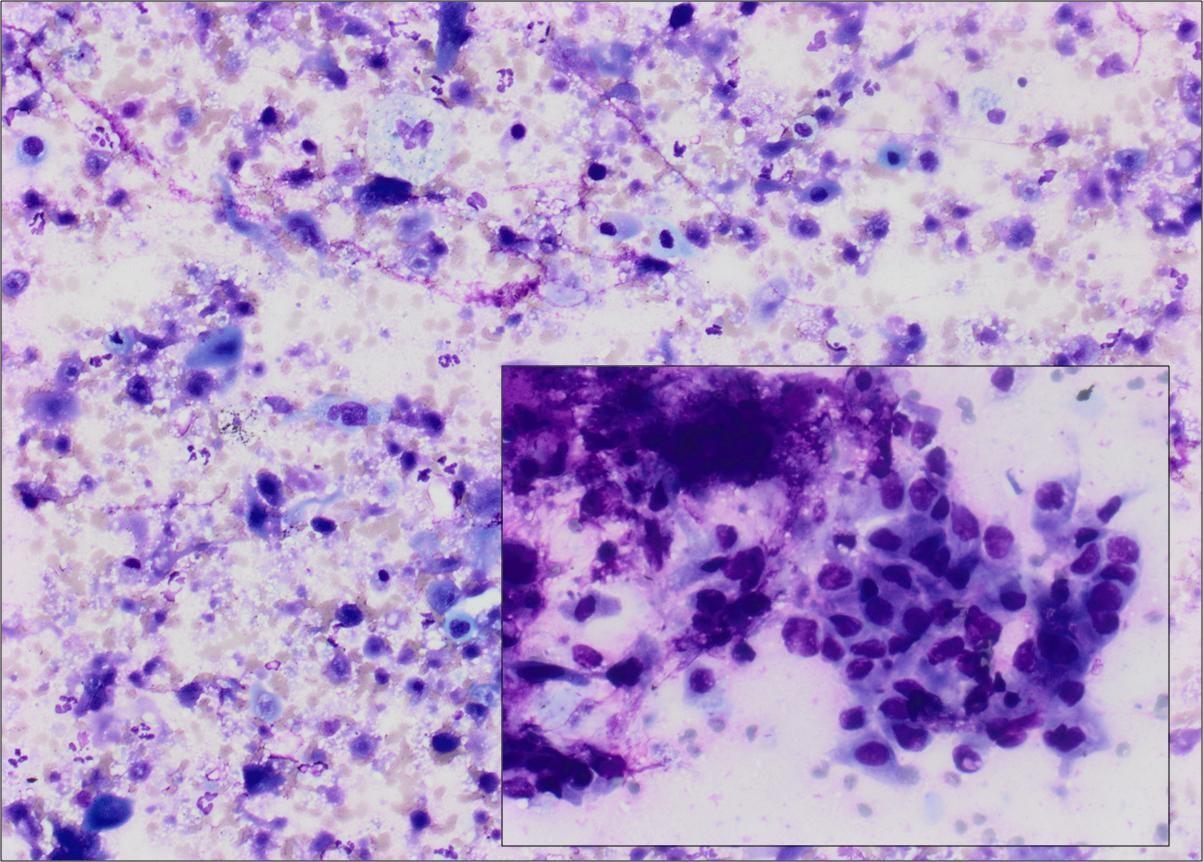
| Lymphoma | Larger immunocytochemistry lymphoma panels Flow cytometry | If possible, use 19 / 20 Gauge procore needle to ensure there are large cores for IHC panels – |
| Metastatic carcinoma | Immunocytochemistry and any molecular testing required i.e. Melanoma – BRAF | Local ICC requirements – dependant on panels used |
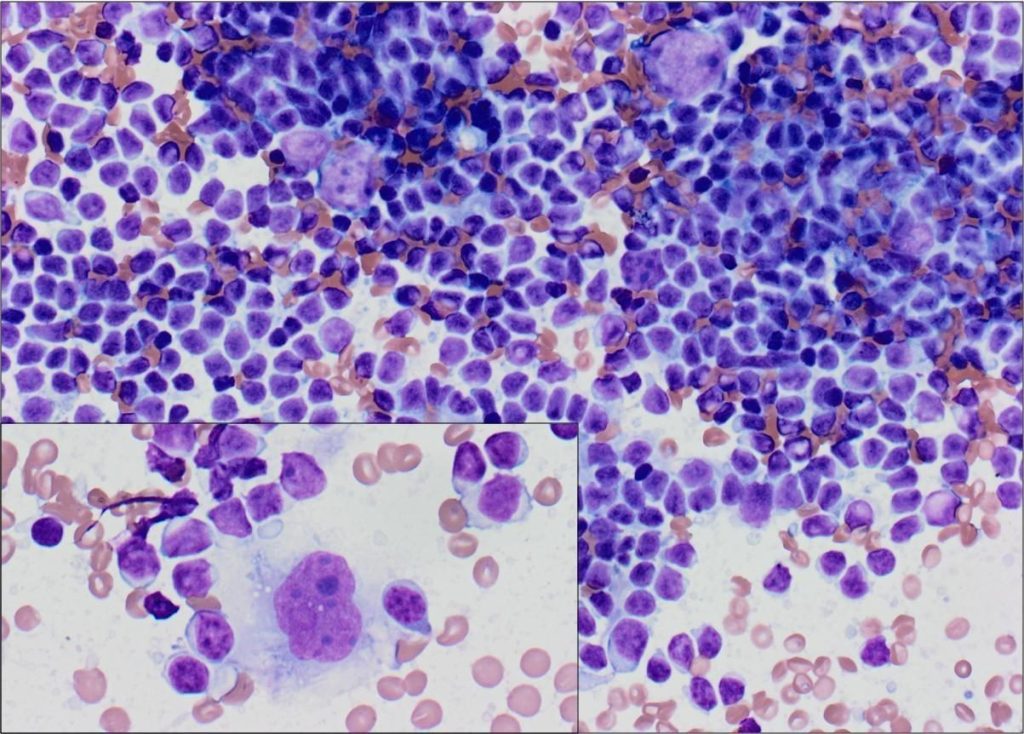
| Lymph node sampling | Not applicable | Minimum of 30% lymphocyte population (More than peripheral blood) Presence of Lymphoglandular bodies Lympho-histocytic aggregates |
| Adequacy criteria guidance | Requirement |
| Morphological appearance | EGFR – Approximately 50% Tumour load to ensure there is enough yield for EGFR (Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor) and ALK (Tyrosine Kinase receptor) testing. In accordance with referral centre protocol |
| Lung Adenocarcinoma | PDL1 – minimum of 100 viable cells (be careful of necrotic lesions) |
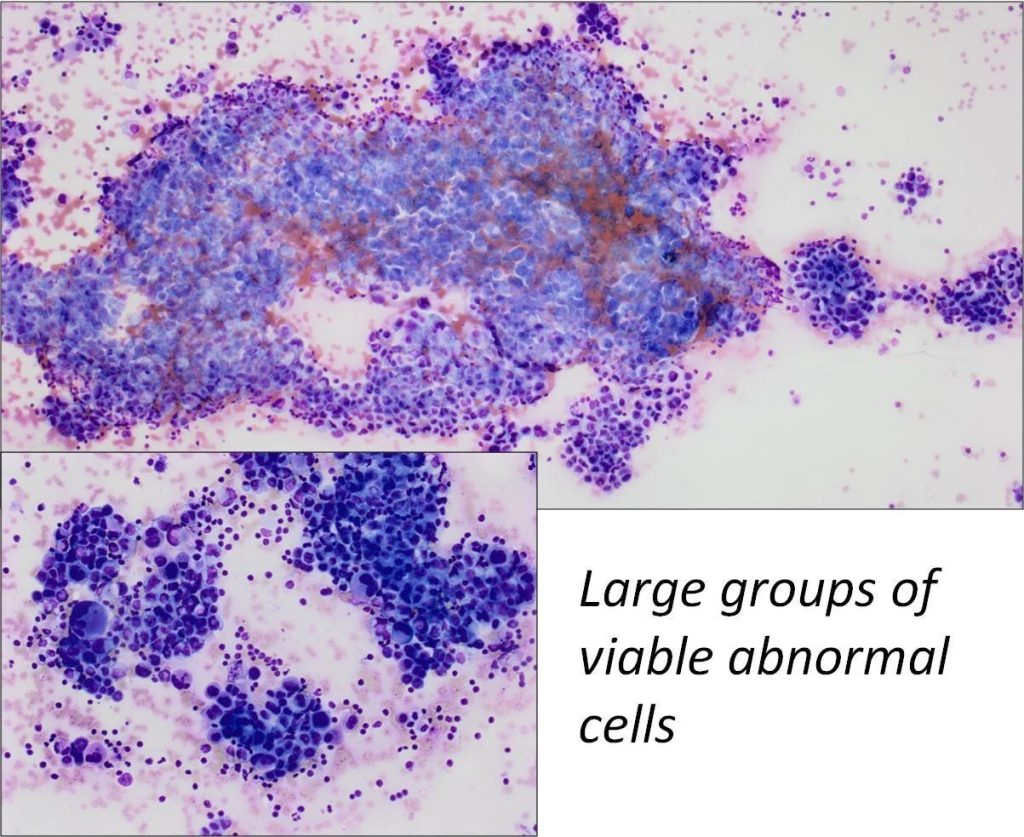
| Necrotic samples | Caution: ensure that atypical single cells are not present within the necrotic debrisAt ROSE necrotic slides can be misinterpreted as cellular. Review on high power to ensure the cells are viable. |
| Lymphoma cases | If possible, use 19 Gauge procore needle to ensure there are large cores for IHC panels. An abundance of lymphocytes is not seen in benign node sampling is seen at ROSE. In some cases, highly atypical cells are also present. |
Images first published: Glinski et al. Single slide assessment: A highly effective cytological rapid on?site evaluation technique for endobronchial and endoscopic ultrasound?guided fine needle aspiration. Cytopathology 30, 164–172 (2019).
Diagnostic pitfalls and considerations
- Contaminant bronchial sampling
- Necrosis, particularly in SCC. Ensure that only viable cells are assessed.
- Process all of the residual material in the laboratory even if the ROSE SSA is inadequate. Subsequent diagnostic material can be found in the induced clot of the residual material. Particularly evident in metastatic renal cell carcinoma where there can be an excess of blood due to the nature of the tumour.
- Streamlined approaches to immunocytochemistry panels must be adopted in laboratory practice for non-small lung carcinoma, to ensure material is not unnecessarily wasted. Standard ICC panel – TTF1, p40 and CK5/6.
- When multiple sites are sampled it crucial that the specifics of the lesion are captured on the form and the corresponding vial and slides – For example in EBUS – Node station numbers are used. Involvement of certain stations can lead to different treatment pathways and prognosis. If staging is being conducted – check that the least suspicious node is sampled first to prevent false positives or inform clinician to use a new needle. Renew all consumables used for ROSE SSA to prevent contamination between samples.
- Fibrotic change due to recent radiotherapy can make it difficult to obtain a cellular sample. Iatrogenic changes must also be taken into consideration.

