Focal and diffuse splenomegalies and FNA
Focal and diffuse splenomegalies and FNA Focal Hodgkins lymphoma Large-cell, non-Hodgkins lymphomas Primary neoplasms and cysts Metastases Tuberculosis Miliary or diffuse Infections Congestive splenomegaly Autoimmune diseses Small-cell, non-Hodgkin lymphomas Histiocytoses Multiple myeloma Myeloproliferative syndromes Leukemias Hemolitic anemias Amyloidosis Fine needle cytology FNC has to be performed using 23-25 gauge needle; the sub-costal approach is […]
Normal constituents
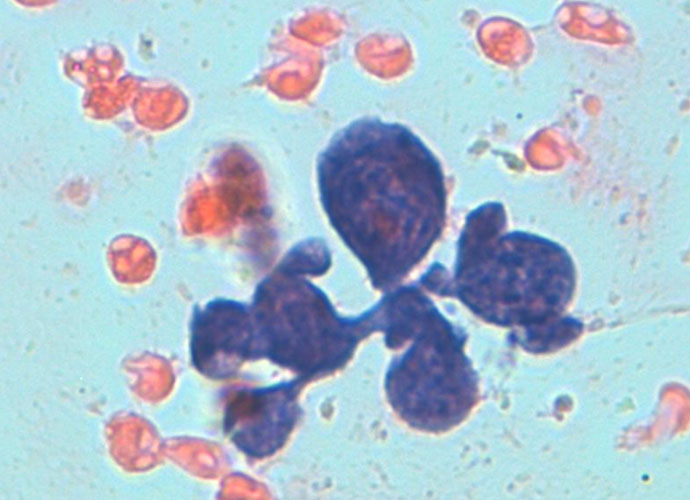
Normal constituents The constituents of the red pulp are generally poorly represented on sFNC, while platelets, macrophages and scattered fibrous or endothelial cells may be observed. The white pulp is represented by dense fragments of tightly packed lymphoid cells, with nuclear details observable only at the edges of the fragments. Invariably one or two vascular […]
White pulp hypeplasia: PALS (T-cells) and follicles (B-cells)
White pulp hypeplasia: PALS (T-cells) and follicles (B-cells) In white pulp hyperplasia smears are highly cellular with numerous and large PALS and dispersed lymphoid cells. White pulp hyperplasia may be observed in infective diseases or immunologic disorders, in children is mainly related to a heightened immunologic state.
Spleen
General Nodular or diffuse splemomegalies may be determined by several causes; in most cases, clinical and serological data are diagnostic but there are still rare conditions or equivocal clinical presentations in which a direct evaluation may be useful. FNC of the spleen was first used for the diagnosis of leishmaniasis and was then extensively used […]

